Manual
5
Similarly, if you place the mirror on the dotted line and look at the image of the word below from the
bottom of the page, what do you see?
---------------------------
DI-OXIDE
An object is said to be SYMMETRICAL about an axis parallel to the mirror surface if the two halves
of the object are mirror images of each other.
• Are the above bold words symmetrical? If so, about which axes?
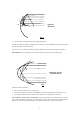
Multiple Reflections - Single Mirror: This experiment requires knowledge of refraction.
Allow a single ray to fall on the plane mirror placed very close to the light-box. Examine the reflected
rays closely.
• How many rays do you observe? Which one is the brightest and which one is the faintest?
• Explain how the images occur?
(HINT: Use the theory of refraction and the fact that the reflecting surface of the mirror is at the
back).
• What happens to the rays as the angle of incidence is
- Decreased from 45° to 0 °?
- Zero?
- Increased from 45 °to 90°?
To study an angle of incidence of 90°, place the mirror so that its side completely covers the slit
and the mirror is parallel to the ray.
• What do you observe at the other side of the mirror?
Rotate the mirror keeping the slit covered by one end of the mirror at all times. What happens?
The above phenomenon is used in OPTICAL FIBERS where light follows a curved path within the
fiber.
Shift the mirror forward and allow the ray to fall on the side of the mirror and observe the mirror from
above.
• How does the above phenomenon occur?
(HINT: Internal reflection)
Multiple Reflections - Multiple Mirrors: Borrow a plane mirror from another light box set. Place the
two mirrors at right angles to each other. Allow a single ray to fall on one of the mirrors. Observe the
ray reflected from the other mirror - it should be parallel to the incident ray.
• Using geometry, explain why this should be so.
• Is this true for all angles of incidence?
• Look into the corner of the mirrors. What do you observe?
If a large plane mirror is available, place it on the table with these two mirrors on it so that all are
mutually pair-wise perpendicular.
• What do you observe in the triple corner?
The above experiment was performed successfully on the moon as well.
• What can you say about the nature of light?
Examine the reflectors at the back of a car. What shape are the dimples in them?