Performance factors for HP ProLiant Serial Attached Storage (SAS)
6
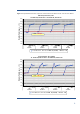
Figure 2. Sequential Write operations with HP Smart Array P411 Controller, RAID 0
Figure 2 illustrates that for write request sizes beginning with 256KiB, an array of midline SAS drives
can write a single stream of data more than twice as fast as a similar array of SATA drives.
Once again, the performance difference is due to a combination of the SATA interface being less
efficient than a SAS interface and to the SATA interface running at 3 Gb/s, while the SAS controller
runs at 6 Gb/s with 6Gb SAS drives.
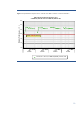
Figure 3 below indicates that an array of midline SAS drives can achieve 20% more random IOPS
than a similar array of SATA drives. (For Figures 3 through 11 comparisons, the X-axis values 1
through 256 represent queue depth.)
In theory the drive, RPM for the SATA and SAS drives are the same. This suggests that the SAS
interface is slightly more efficient, resulting in a small performance increase.
The observed difference may result from the drives’ physical characteristics (for example, elevator
sorting.) Another factor may be the limits the SA controller sets on the SATA drive queue depth. The
difference should not influence performance of small-block random workloads.
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
4KiB 64KiB 256KiB 512KiB 1MiB
Midline SATA
Midline SAS
Sequential Write, RAID-0, 12 Drives
MiB/s