Linux Best Management Practices for HP ProLiant Gen8 Servers and Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Technical white paper | Linux Best Management Practices: HP ProLiant Gen8 Servers and Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Overview
One of the most significant new features of the HP ProLiant Gen8 servers is support of Agentless Management. Prior to introducing this
feature, traditional management systems required SNMP agents and similar software to run on the OS. Now, when iLO 4 is configured
for Agentless Management, it runs an SNMP agent, allowing the HP ProLiant Gen8 host to be agentless (no SNMP agent needs to run
on the host OS). HP ProLiant Gen8 Servers provide SNMP v1 agents that run on the Integrated Lights-Out 4 (iLO 4) management
controller. The iLO SNMP management agents provide access to SNMP elements that are important to the overall condition of the
server, even when the server is powered off or in the process of starting the operating system. Once the iLO network cable is plugged in
and the server powered up, the server is inherently manageable via iLO. The iLO monitors the health of the server and sends SNMP
alerts.
HP provides an Agentless Management Service (AMS) for Red Hat Enterprise Linux that allows iLO 4 to support host-related SNMP
entities. The iLO 4 SNMP agent communicates with HP AMS on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux host. The Agentless Management Service
provides iLO 4 with valuable information about the operating system.
HP ProLiant Gen8 servers continue to provide the powerful manageability features notable with previous HP ProLiant generations. With
the additional support of HP AMS, the HP ProLiant Gen8 servers provide powerful core management functionality for internal system
components (including health monitoring and alerting directly from the iLO). What is more, this functionality is provided without any
drivers or agents having to be installed on the host. HP AMS provides significant advantages, including:
• Enabling simpler and easier installation and configuration
• Allowing hardware management processes to continue functioning independently of the host processor and OS, and regardless of the
state of the OS
• Increasing security and stability because the management software and possible vulnerabilities are moved away from the host OS to
the ILO hardware
• Consuming less memory and fewer processor cycles compared to in-band SNMP agents
• Separating the management network from the application data network without sacrificing a system network port (HP AMS provides
configuration, monitoring, and alerting data through the iLO NIC)
These and other advantages are described in more detail in the sections that follow.
You can view the data that the iLO 4 Agentless Management collects by using the web-based iLO 4 GUI, the iLO XML scripting
interface, or a remote management application such as HP Systems Insight Manager (HP SIM).
The HP AMS feature is optional. HP ProLiant Gen8 servers can still use the legacy SNMP agents as before. Although HP AMS is a great
solution for a majority of HP ProLiant environments, certain usage scenarios may still require SNMP agents. For more information, see
“Running HP AMS and legacy SNMP agents”. This paper describes the HP Agentless Management Service provided for Red Hat
Enterprise Linux operating systems, iLO 4 Agentless Management, and configuration options. It explains how to configure and install HP
AMS, and how to run HP AMS or legacy agents to support the needs of your server environment. Appendices list the SNMP elements
supported by HP AMS and iLO 4, and the traps generated by HP AMS and iLO 4.
Comparing HP Agentless Management with OS-based management
OS-based management
For earlier generations of the HP ProLiant server and other traditional non-HP servers, a standard SNMP service and related software
must be installed on the OS and must run under the domain of the OS to provide management functionality. The SNMP service collects
server-specific, OS-specific, and industry-standard data. It bundles the data and makes it available to the System Management
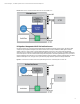
Homepage (SMH) or a remote management application, such as HP SIM. Figure 1 shows an example of a server with the traditional
OS-based SNMP agents interacting with HP SIM.
In addition to supporting traditional SNMP elements (MIB-II), the standard SNMP service provides sub-agents to support HP enterprise
elements. (For a list of supported SNMP elements, see “Appendix A: SNMP elements supported by iLO 4 and HP AMS”.) Some of the
HP enterprise elements use data provided by the HP ProLiant iLO Baseboard Management Controller (BMC). The BMC monitors the
overall health and condition of the physical server. As shown in Figure 1, the iLO BMC collects health data. HP SIM obtains some
information about the system from the iLO BMC, but it obtains health data by running SNMP queries against the SNMP agent. The
SNMP agent runs on the host OS and must obtain the health data from the iLO BMC.
2