Building Disaster Recovery Serviceguard Solutions Using Metrocluster with Continuous Access XP P9000 for Linux B.12.00.00
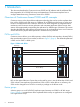
Figure 2 Journal Volume
Primary
Data Volume
Issuing Read
Journal Command
Journal Copy
Function
Primary Host Secondary Host
Master
Journal Volume
Journal
obtain function
Primary Storage System
Site A Site B
Secondary
Data Volume
Restore
Journal Volume
Journal
restore function
Secondary Storage System
By writing the records to journal disks instead of keeping them in cache, Continuous Access Journal
overcomes the limitations of earlier asynchronous replication methods. Writes to the journal are
cached for application, but are quickly de-staged to disk to minimize cache usage.
In addition to the records being replicated, the journal contains metadata for every record to ensure
the integrity and consistency of the replication process. Every transmitted record set includes both
time stamp and sequence number information, which enables the replication process to verify that
all the records are received at the remote site, and to arrange them in the correct write order for
storage. These processes build on the proven algorithms of XP or P9000 Continuous Access
Asynchronous Data Replication. The journaling and replication processes also support consistency
across multiple volumes.
For more information, see the guide HP P9000 Continuous Access Journal User Guide available
at http://www.hp.com/support/manuals -> storage-> Storage Software-> Storage Replication
Software -> HP P9000 Continuous Access Software or HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000
Continuous Access Journal Software User Guide available at http://www.hp.com/support/
manuals -> storage-> Storage Software-> Storage Replication Software -> HP XP Continuous Access
Software.
Fence level
The Continuous Access Journal has the asynchronous data replication characteristic. The fence
level of the Continuous Access journal is set to “async”, similar to the Continuous Access
Asynchronous fence level.
Mitigation of network problems
In Continuous Access Asynchronous replication, typical issues include temporary communication
problems, such as Continuous Access link failure or insufficient bandwidth for peak-load
requirements. These conditions can cause cache-based “push” replication method to fail. When
this happens, traditional replication solutions suspend the replication process and go into bitmap
Overview of Continuous Access P9000 and XP concepts 9