HP StorageWorks Storage Mirroring evaluation guide (T2558-96075, February 2008)
1 - 4
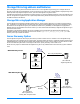
Failure monitoring and failover
Failover is the process in which a target stands in for a failed source. As a result, user and application requests that are directed
to the failed source are routed to the target.
Storage Mirroring monitors the source status by tracking network requests and responses exchanged between the source
and target. When a monitored source misses a user-defined number of requests, Storage Mirroring assumes that the server
has failed. Storage Mirroring then prompts the network administrator to initiate failover, or, if configured, it occurs
automatically.
The failover target assumes the network identity of the failed source. When the target assumes the identity of the source,
user and application requests destined for the source server or its IP address(es) are routed to the target.
When partnered with the Storage Mirroring data replication capabilities, failover routes user and application requests with
minimal disruption and little or no data loss. In some cases, failover may be used without data replication to ensure high
availability on a server that only provides processing services, such as a web server.
Source
Target
User and application requests
sent to the source name or IP address
Mirroring and replicating data
Failure monitoring
Before failover occurs
Source
Target
User and application requests
sent to the source name or IP address
After failover occurs
which is now running o the target
X