hostname.1 (2010 09)
h
hostname(1) hostname(1)
NAME
hostname - set or display name of current host system
SYNOPSIS
hostname [name_of_host ]
DESCRIPTION
The
hostname command displays the name of the current host, as given in the
gethostname()
sys-
tem call (see gethostname (2)). Users who have appropriate privileges can set the hostname by giving the
argument name_of_host ; this is usually done in the startup script
/sbin/init.d/hostname
. The
name_of_host argument is restricted to
MAXHOSTNAMELEN
characters as defined in
<sys/param.h>.
The system might be known by other names if networking products are supported. See the node manager
documentation supplied with your system.
WARNINGS
If the name_of_host argument is specified, the resulting host name change lasts only until the system is
rebooted. To change the host name permanently, run the special initialization script
/sbin/set_parms
(see Using Your HP Workstation).
Many types of networking services are supported on HP-UX, each of which uses a separately assigned
system name and naming convention. To ensure predictable system behavior, it is essential that system
names (also called host names or node names) be assigned in such a manner that they do not create
conflicts when the various networking facilities interact with each other.
The system does not rely on a single system name in a specific location, partly because different services
use dissimilar name formats as explained below. The
hostname and uname commands assign system
names as follows:
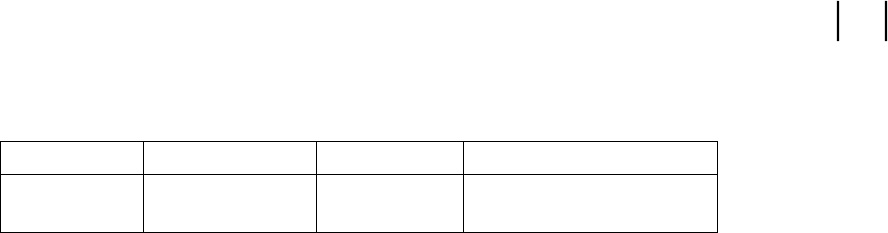
Node Name Command name Format Used By
Internet name hostname name sys[.x.y.z...] ARPA and NFS Services
UUCP name uname -S name sys uucp and related programs
where sys represents the assigned system name. It is strongly recommended that sys be identical for all
commands and locations and that the optional .x.y.z... follow the specified notation for the particular
ARPA/NFS environment.
Internet names are also frequently called host names or domain names (which are different from NFS
domain names). Refer to hostname (5) for more information about Internet naming conventions.
Whenever the system name is changed in any file or by the use of any of the above commands, it should
also be changed in all other locations as well. Other files or commands in addition to those above (such as
/etc/uucp/Permissions
if used to circumvent uname, for example) may contain or alter system
names. To ensure correct operation, they should also use the same system name.
System names are normally assigned by the
/sbin/init.d/hostname script at start-up, and should
not be altered elsewhere.
Setting a hostname of more than 64 bytes is possible only with the appropriate configuration options
enabled. It is strongly recommended that all related documentation be completely understood before set-
ting a larger hostname. A hostname larger than 64 bytes can cause anomalous or incorrect behavior in
applications which use the
hostname command or the gethostname() system function to access the
name.
AUTHOR
hostname was developed by the University of California, Berkeley.
SEE ALSO
uname(1), gethostname(2), sethostname(2), uname(2), hostname(5), nodehostnamesize(5).
Using Your HP Workstation
HP-UX 11i Version 3: September 2010 − 1 − Hewlett-Packard Company 1


