Operating Instructions
RQT8173
21
Using with other equipment
Before use
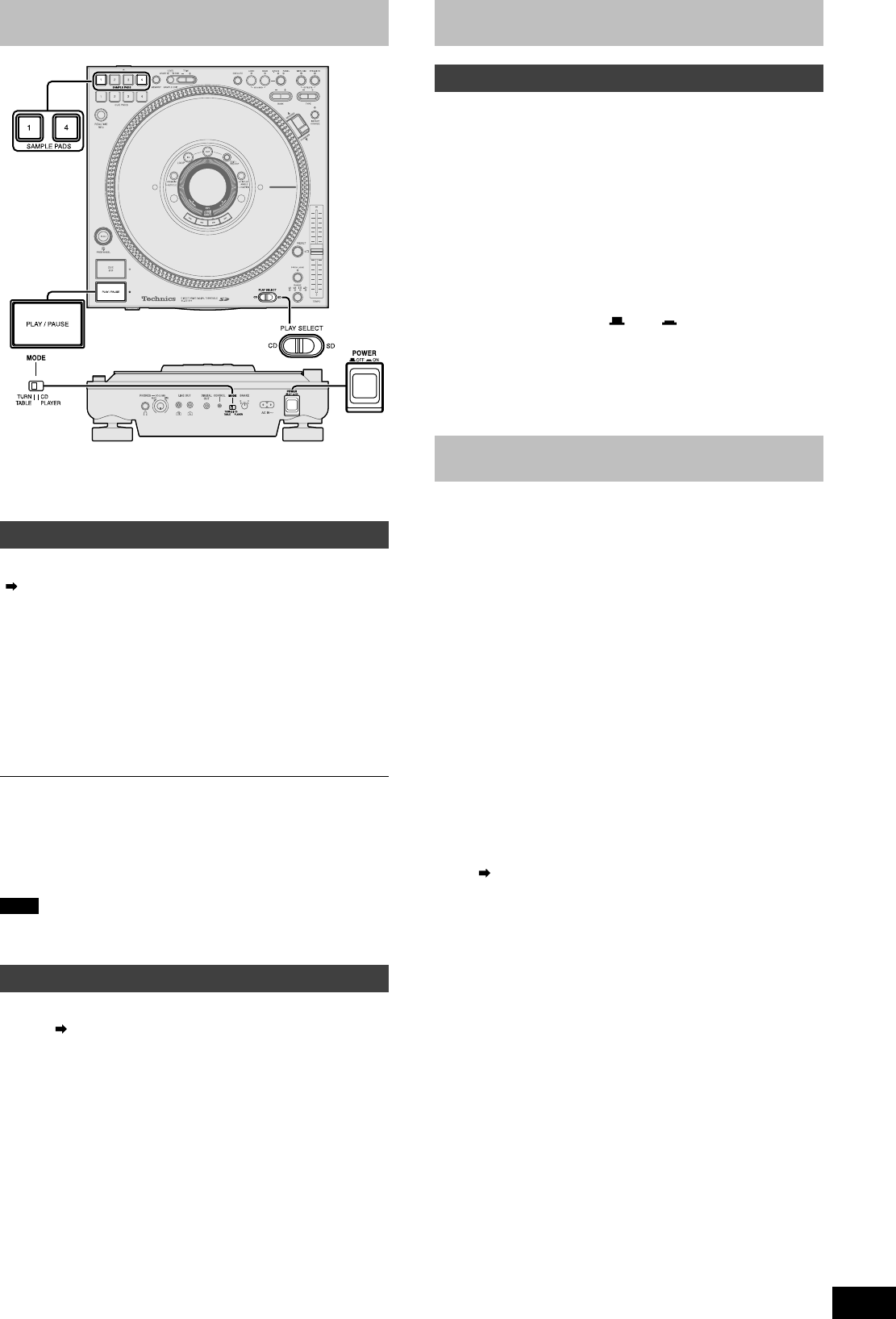
•Switch [PLAY SELECT] to select the media to be used
•Turn [MODE] on the rear panel to TURNTABLE
•Insert the SD Memory Card or CD to be used
You can relay play by connecting the control terminals of the two units.
( page 7)
Before use:
•Turn Auto Cue on for both units, set the auto cue point for the track
to be played and back cue.
Using two units for relay play
Press [PLAY/PAUSE] on the unit to be
played first
•Once track play finishes on the unit being played, play auto-
matically begins from the unit on standby.
•The unit that was played first pauses and cues at the next track’s
auto cue point.
•You can automatically alternate play between both units by repeat-
ing this method.
•You can listen to many different tracks by changing the media and
selecting the track of the unit in the standby position.
•Set the cue point, select the cue bank and back cue on the standby
unit to begin relay play from the desired point of the desired track.
Note
•During play, if power on one of the units is cut or turned off, play
may begin on the other standby unit.
Using the amplifier and other equipment
Connect with the matching input terminals on the equipment (not in-
cluded). ( page 7)
•When using this unit’s DIGITAL OUT terminal, SD Audio is not out-
put.
1 Put the equipment on standby
2 Press [PLAY/PAUSE] to play
•Audio played from the connected equipment is output.
Initializing this unit’s memory
Unit’s initialize memory function
You can re-initialize all memory content on this unit, restoring it to
factory settings.
Re-initializing will erase the following memory.
•Cue bank, cue pad, loop play
•Vinyl simulator, dynamic effect settings
•Auto Cue on, off settings and auto cue level settings
•Instant change settings
50 CDs or SD Memory Cards worth of data items of the above indi-
cated media data.
•Display angle, display contrast settings
When the power is off
While holding down [SAMPLE PADS 1] and [SAMPLE
PADS 4], press [POWER
OFF ON] to turn the power
on, and release [SAMPLE PADS 1] and [SAMPLE PADS
4] after “INITIALIZED” appears in the display
•All memory content is re-initialized.
•The display returns to its original state and you can begin operat-
ing.
Glossary
•SD Audio
An audio standard for SD Memory Cards. An encryption technology is
used in order to protect copyrights and the legal rights of the con-
sumer as well as help develop a healthy music culture. There are
restrictions upon the copying of data etc. Use an application like SD-
Jukebox etc. for creating data.
•Cue
Used to begin play. On this unit the cue point is used to store the
beginning of a track or an arbitrary point of a track to memory and
then to instantly begin play from this point.
•Platter slip surface
The rotatable surface on an analogue turntable which you place a
record. Although this unit is a digital turntable, play functionality is the
same as when operating a platter slip surface on an analogue turn-
table.
•MP3 album
When creating multiple MP3 files on a computer and writing to a CD-
ROM, you can organize the files using folders. These folders are called
albums on this unit. When you want to play tracks in sequential order
on this unit, use numbers like 001 and 002 etc. for naming the al-
bums. ( Page 20)
•AAC
A compression standard that makes recording and play of high qual-
ity audio possible including MPEG2 (an international standard). Used
in SD Audio and broadcast satellite digital signals.
•MP3
MP3 is the abbreviated form of the international standard MPEG1/
Audio Layer3. MP3 allows you to achieve approximately ten to one
compression rates with bit rates of 128 kbps. MP3 is used widely with
SD Audio, CDs, and computers.
•Sampling frequency
The number of samples taken approximately each second when an
audio signal is digitally converted and stored in memory. The higher
the value the wider the frequency range can be used for digital con-
version thus providing near original audio quality reproduction, how-
ever the resulting size of the audio data does become quite large.
•Bit rate
A value that indicates the audio signal compression rate. Indicates
the number of bits sampled approximately each second, the larger
the bit value the more information is contained resulting in better au-
dio quality, however the size of the audio data does become quite
large.










