User Manual
0.1C or below, or intermittent discharge
0.17C or current close to it
0.26C or current close to it
0.6C or current close to it
Current in excess of 3C
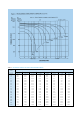
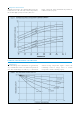
For intermediate values, see figure 3 on page 6
1.75
1.70
1.67
1.60
1.30
see figure 3 on page 6
Table 6. DISCHARGE CAPACITY AT VARIOUS DISCHARGE RATES
– 8 –
Over Discharge (Deep Discharge)
The dotted line in Figure 3 indicates the lowest
recommended voltage under load, or cut off voltage, for
NP batteries at various discharge rates. In general, lead
acid batteries are damaged in terms of capacity and
service life if discharged below the recommended cut off
voltages. It is generally recognised that all lead calcium
alloy grid batteries are subject to over discharge damage.
For example, if a lead acid battery were discharged to
zero volts, and left standing in either “on” or “off” load
conditions for a long period of time, severe sulphation
would occur, raising the internal resistance of the battery
abnormally high. In such an extreme case, the battery
may not accept charge. NP batteries have been designed
to withstand some levels of over-discharge. However,
whilst this is not the recommended way of operation,
Yuasa NP batteries can recover their capacity when
recharged correctly. Final discharge voltage is shown in
Table 7.
Table 7. FINAL DISCHARGE VOLTAGE
If a battery is to be discharged at a rate in excess of
3C Amps, please contact us prior to use.
Discharge Current Final Discharge Voltage (V/Cell)