User manual
Table Of Contents
- Table of Contents
- About This Guide
- Introduction
- ISDN LAN Modem Functionality Description
- Hardware Description and Installation
- Setting Up TCP/IP for Windows and Macintosh
- Configuring the ISDN LAN Modem
- Advanced Configuration
- Before you Begin
- Setting Up Additional Service Providers
- Editing Service Provider Profiles
- Restricting Workstations from Accessing Service Provider(s)
- Configuring Your LAN Parameters
- Changing Data Call Parameters
- Changing Voice Call Routing
- Reserving DHCP Addresses
- Selective Password Protection
- Changing Your Password
- Setting Up Your ISDN Line Manually
- Locking and Unlocking the Configuration
- Configuring the ISDN LAN Modem from a Remote Location
- Supplementary Voice Call Services
- Placing, Receiving and Disconnecting Calls
- Troubleshooting and Maintenance
- Networking Primer
- What is a network?
- What is a LAN?
- What is a WAN?
- How does a LAN connect to a WAN?
- What is a LAN modem?
- What is ISDN?
- How do different devices communicate with each other?
- What is TCP/IP?
- What is an IP Address?
- What is a Subnet Mask?
- Dynamic and Static IP Addresses
- What is DHCP?
- What is DNS?
- What is NAT?
- What are numbered and unnumbered links?
- How is overall throughput determined?
- What is a network?
- Using the Custom Web Browser
- ISDN LAN Modem Factory Defaults
- ISDN LAN Modem Specifications
- Ordering ISDN Service
- If You Place Your ISDN Order Through 3Com
- If You Place Your ISDN Order Through the Telephone Company
- Supplementary Voice Features Included with U, EZ-ISDN-1, V and EZ-ISDN 1A
- Limitations of ISDN Ordering Codes U, EZ-ISDN 1, V and EZ-ISDN 1A
- What If I Already Have ISDN Service?
- Table of ISDN Ordering Code Capabilities
- Glossary
- Index
- 3Com Corporation Limited Warranty
A
N
ETWORKING
P
RIMER
This chapter provides a description of basic networking concepts and terminology
to help you better understand the key functionality of the ISDN LAN Modem.
What is a network?
A network is a set of computers and other devices such as printers, modems, and
scanners that are connected together either directly via physical cables or indirectly
via dial-up telephone services. A network can be in the same room, the same
building covering a local area, or geographically dispersed covering a wide area.
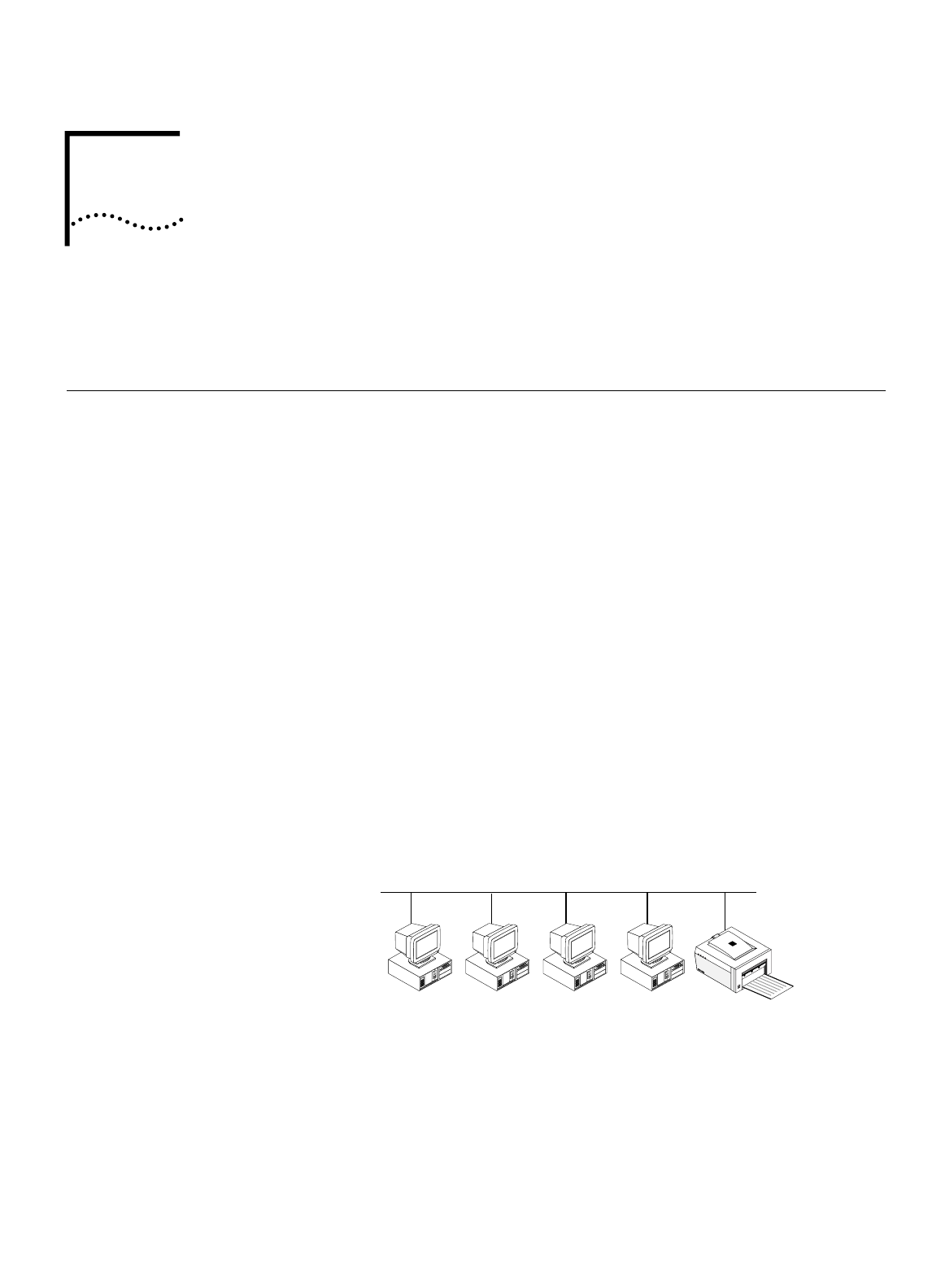
What is a LAN?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is two or more computers linked together in a
contained location such as an office building. By linking the computer together,
and creating a LAN, users can share files and share access to printers.
To physically create a LAN, each computer must be linked together using some
type of cabling. Typically, Ethernet cabling is used. There are three main types of
Ethernet networks: 10BASE-T, 10BASE-2 and 10BASE-5. The ISDN LAN Modem
supports four 10BASE-T connections.
A 10BASE-T Ethernet network is used in small networks with only a few dozen
devices closely located. The physical connection for a 10BASE-T Ethernet network
is over a twisted pair cable. The connector used for 10BASE-T looks similar to the
connector used for your telephone. A 10BASE-5 Ethernet network is used in large
networks with many devices where transmissions occur over distant geographic
areas. A 10BASE-2 (Thin) Ethernet network is used in smaller networks with all
devices being relatively close together.
Figure 53
Example of a LAN
What is a WAN?
A Wide Area Network is the result of the connection of two or more LANs,
typically using dial up telephone services via a modem and usually over far
geographic distances.
10 Mbps Ethernet LAN
N
e
t
w
o
r
k
s
T
h
a
t
G
o
t
h
e
D
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
3 Com










