User manual
Table Of Contents
- Table of Contents
- About This Guide
- Introduction
- ISDN LAN Modem Functionality Description
- Hardware Description and Installation
- Setting Up TCP/IP for Windows and Macintosh
- Configuring the ISDN LAN Modem
- Advanced Configuration
- Before you Begin
- Setting Up Additional Service Providers
- Editing Service Provider Profiles
- Restricting Workstations from Accessing Service Provider(s)
- Configuring Your LAN Parameters
- Changing Data Call Parameters
- Changing Voice Call Routing
- Reserving DHCP Addresses
- Selective Password Protection
- Changing Your Password
- Setting Up Your ISDN Line Manually
- Locking and Unlocking the Configuration
- Configuring the ISDN LAN Modem from a Remote Location
- Supplementary Voice Call Services
- Placing, Receiving and Disconnecting Calls
- Troubleshooting and Maintenance
- Networking Primer
- What is a network?
- What is a LAN?
- What is a WAN?
- How does a LAN connect to a WAN?
- What is a LAN modem?
- What is ISDN?
- How do different devices communicate with each other?
- What is TCP/IP?
- What is an IP Address?
- What is a Subnet Mask?
- Dynamic and Static IP Addresses
- What is DHCP?
- What is DNS?
- What is NAT?
- What are numbered and unnumbered links?
- How is overall throughput determined?
- What is a network?
- Using the Custom Web Browser
- ISDN LAN Modem Factory Defaults
- ISDN LAN Modem Specifications
- Ordering ISDN Service
- If You Place Your ISDN Order Through 3Com
- If You Place Your ISDN Order Through the Telephone Company
- Supplementary Voice Features Included with U, EZ-ISDN-1, V and EZ-ISDN 1A
- Limitations of ISDN Ordering Codes U, EZ-ISDN 1, V and EZ-ISDN 1A
- What If I Already Have ISDN Service?
- Table of ISDN Ordering Code Capabilities
- Glossary
- Index
- 3Com Corporation Limited Warranty
What is a network? 107
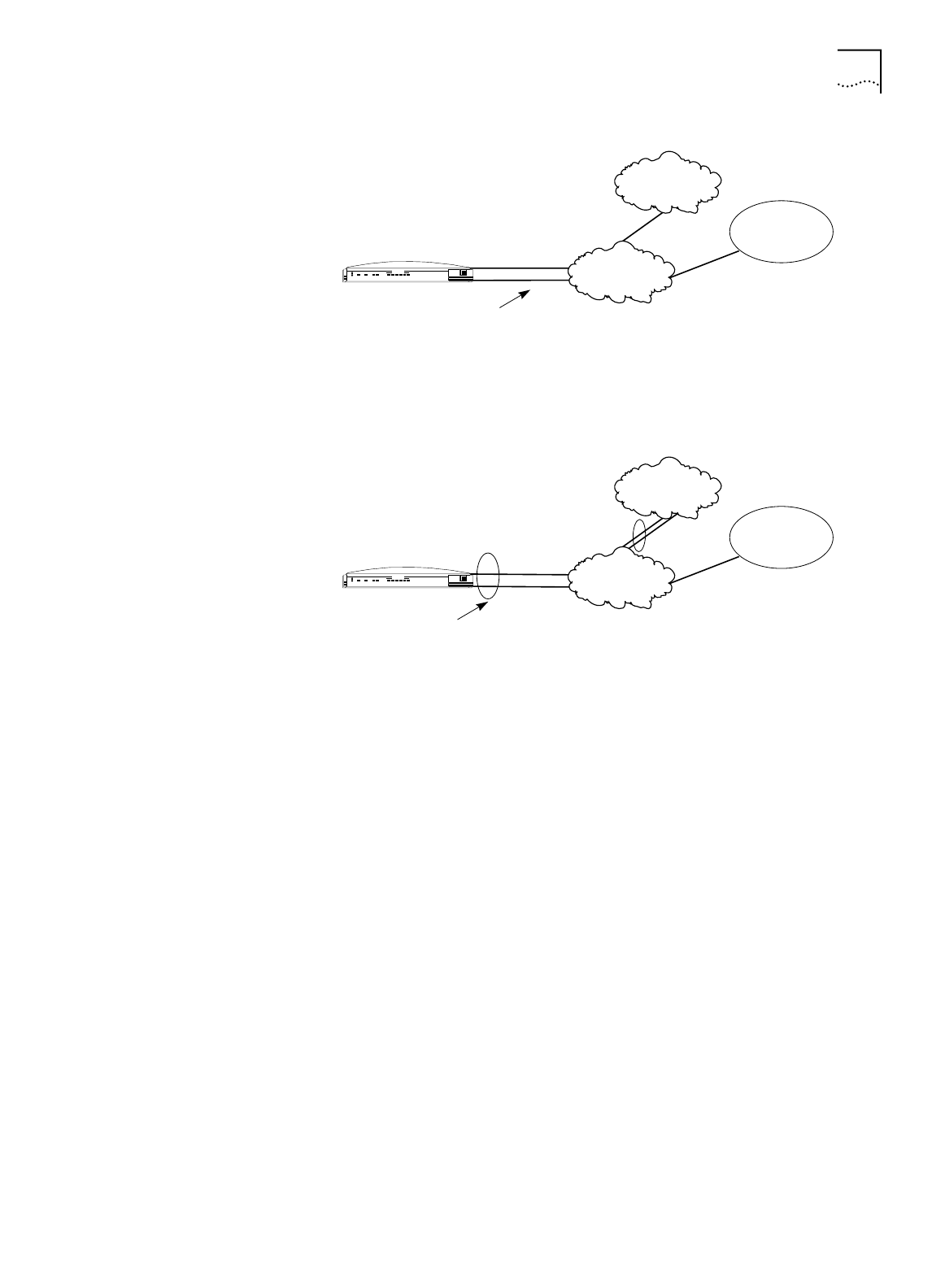
Figure 56
Two Simultaneous Connections
The B channels may also be combined using the Multilink PPP feature to allow one
higher speed connection to a single location as shown in Figure 57.
Figure 57
Using Multilink to Combine B Channels for a Single High-Speed Link
How do different
devices communicate
with each other?
Once the computers are physically connected in a network, they must run some
type of standard communications software that allows different types of
computers to communicate with each other. Transmission Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is becoming the most common software used
to accomplish this.
What is TCP/IP? TCP/IP is a standardized communications protocol that works across LANs and
WANs, allowing different devices to communicate with each other. As its name
indicates, TCP/IP has two main components, TCP and IP. TCP manages the transfer
of data and corrects any errors that occur during transmission. It ensures that data
is reliably transferred. IP routes the data in packets from one location to another
across a network using the source and destination information within each data
packet to determine routing and destinations.
Note that TCP/IP encompasses more than the two protocols which define its
name. It comprises a set of software applications that allow various network
services such as remote file transfer protocol (FTP), remote login (Telnet), and
e-mail Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and Post Office Protocol (POP) 3.
Public telephone
network
Remote office
LAN
ISDN BRI line
Internet/Intranet or
online service
PWR
ISDN
B1
B2
3 Com
Alert
Tx
Coll
1
2 3 4
LAN STATUS
B channel 1
B channel 2
B channel 1
B channel 2
OfficeConnect
¤
ISDN LAN Modem
OfficeConnect
®
ISDN LAN Modem
Public telephone
network
Remote office
LAN
Combining both
B channels with Multilink
provides a single 128 Kbps*
connection
Internet/Intranet or
online service
PWR
ISDN
B1
B2
3 Com
Alert
Tx
Coll
1
2 3 4
LAN STATUS
64 Kbps B1
64 Kbps B2
128 Kbps B1 & B2
*Without compression.
OfficeConnect
¤
ISDN LAN Modem
OfficeConnect
®
ISDN LAN Modem










