User manual
Table Of Contents
- Table of Contents
- About This Guide
- Introduction
- ISDN LAN Modem Functionality Description
- Hardware Description and Installation
- Setting Up TCP/IP for Windows and Macintosh
- Configuring the ISDN LAN Modem
- Advanced Configuration
- Before you Begin
- Setting Up Additional Service Providers
- Editing Service Provider Profiles
- Restricting Workstations from Accessing Service Provider(s)
- Configuring Your LAN Parameters
- Changing Data Call Parameters
- Changing Voice Call Routing
- Reserving DHCP Addresses
- Selective Password Protection
- Changing Your Password
- Setting Up Your ISDN Line Manually
- Locking and Unlocking the Configuration
- Configuring the ISDN LAN Modem from a Remote Location
- Supplementary Voice Call Services
- Placing, Receiving and Disconnecting Calls
- Troubleshooting and Maintenance
- Networking Primer
- What is a network?
- What is a LAN?
- What is a WAN?
- How does a LAN connect to a WAN?
- What is a LAN modem?
- What is ISDN?
- How do different devices communicate with each other?
- What is TCP/IP?
- What is an IP Address?
- What is a Subnet Mask?
- Dynamic and Static IP Addresses
- What is DHCP?
- What is DNS?
- What is NAT?
- What are numbered and unnumbered links?
- How is overall throughput determined?
- What is a network?
- Using the Custom Web Browser
- ISDN LAN Modem Factory Defaults
- ISDN LAN Modem Specifications
- Ordering ISDN Service
- If You Place Your ISDN Order Through 3Com
- If You Place Your ISDN Order Through the Telephone Company
- Supplementary Voice Features Included with U, EZ-ISDN-1, V and EZ-ISDN 1A
- Limitations of ISDN Ordering Codes U, EZ-ISDN 1, V and EZ-ISDN 1A
- What If I Already Have ISDN Service?
- Table of ISDN Ordering Code Capabilities
- Glossary
- Index
- 3Com Corporation Limited Warranty
Understanding Multilink PPP and BACP/BAP 21
Figure 9
IP Address Translation
Call Routing While One Call Is Already Connected
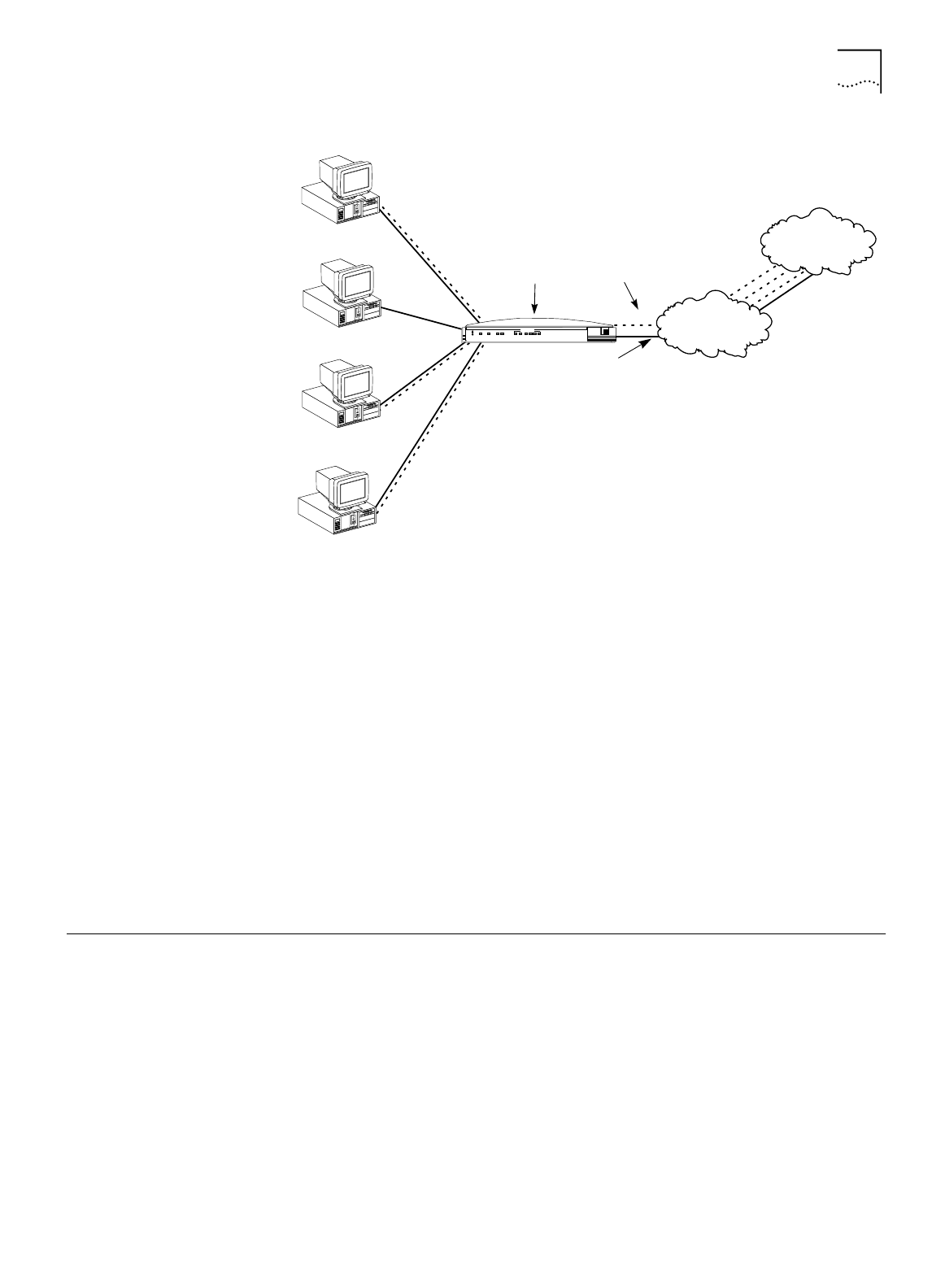
If the ISDN LAN Modem has established a call to a remote destination, for
instance, to an ISP, and the ISDN LAN Modem receives more packets, then the
ISDN LAN Modem looks at the Network ID of the packets for proper routing. For
example, if the Network ID of the packets matches that of the remote LAN and
that connection has not yet been established, then the call is placed and the
connection is made. If the Network ID does not match and the call type is an
Internet access call, then the packets are routed to the ISP.
Note that the ISDN LAN Modem always calls the first configured ISP. If you have
configured a second ISP and want to use that one instead, from the ISDN LAN
Modem’s configuration home page go to
Workstation Parameters
, select your
computer, and then associate only the ISP that you want to use.
Understanding
Multilink PPP and
BACP/BAP
What is Multilink PPP?
Multilink PPP is a protocol which combines multiple point-to-point protocol (PPP)
connections to form a single high-bandwidth channel. With a BRI line, Multilink
PPP combines the two 56 Kbps or 64 Kbps ISDN B channels, creating a virtual,
single connection of up to 112 Kbps or 128 Kbps.
What is BACP/BAP?
BACP/BAP is used in conjunction with the Multilink PPP feature and is transparent
to the user (that is, it will not be visible to you as it occurs in the background). You
need not configure this functionality. When Multilink PPP is negotiated, the
Bandwidth Allocation Control Protocol (BACP) negotiates with the peer
equipment to determine whether the peer supports BAP. If the peer supports BAP
198.6.1.1
198.6.1.1
198.6.1.1
192.168.1.5
192.168.1.2
192.168.1.4
OfficeConnect
®
ISDN LAN Modem
192.168.1.1
ISDN BRI line
Internet/Intranet or
online service
PWR
ISDN
B1
B2
3 Com
Alert
Tx
Coll
1
2 3 4
LAN STATUS
Rob's PC
192.168.1.2
Laura's PC
192.168.1.3
Buddy's PC
192.168.1.4
Sally's PC
192.168.1.5
198.6.1.1
IP address
assigned by ISP
Translates PC IP
addresses to IP
address assigned
by ISP
ISDN BRI line
Public telephone
network
OfficeConnect™
ISDN LAN Modem










