User's Manual Part 1
Table Of Contents
- About This Guide
- Introducing the Gateway
- Hardware Installation
- Setting Up Your Computers
- Running the Setup Wizard
- Gateway Configuration
- Troubleshooting
- Using Discovery
- IP Addressing
- Technical Specifications
- Safety Information
- End User Software License Agreement
- ISP Information
- Glossary
- 802.11b
- 802.11g
- 10BASE-T
- 100BASE-TX
- Access Point
- Ad Hoc mode
- Auto-negotiation
- Bandwidth
- Category 3 Cables
- Category 5 Cables
- Channel
- Client
- DHCP
- DNS Server Address
- DSL modem
- Encryption
- ESSID
- Ethernet
- Ethernet Address
- Fast Ethernet
- Firewall
- Full Duplex
- Gateway
- Half Duplex
- Hub
- IEEE
- IETF
- Infrastructure mode
- IP
- IP Address
- ISP
- LAN
- MAC
- MAC Address
- NAT
- Network
- Network Interface Card (NIC)
- Protocol
- PPPoE
- PPTP
- RJ-45
- Server
- SSID
- Subnet Address
- Subnet mask
- Subnets
- Switch
- TCP/IP
- Traffic
- universal plug and play
- URL Filter
- WAN
- WECA
- WEP
- Wi-Fi
- Wireless Client
- Wireless LAN Service Area
- Wizard
- WLAN
- WPA
- Glossary
- Regulatory Notices for the Wireless 11g Cable/DSL Gateway
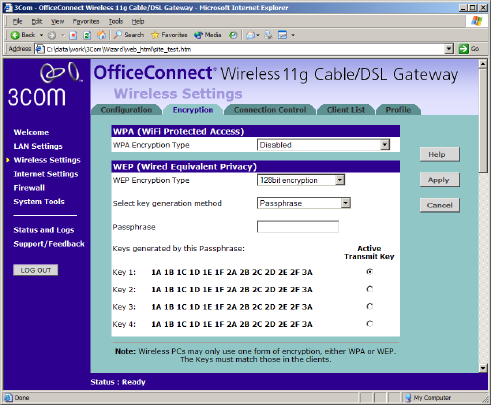
Wireless Settings 51
Encryption Keys
Figure 34 Encryption Keys Screen showing WEP configuration
A Key is a hexadecimal (0-9, A-F) number used to encrypt and decrypt the
data. There can be up to 4 keys and each key can be as long as 26 digits.
The Gateway also offers a number of methods for converting plain text
into hex keys. The text is much easier to remember than hex keys but it
relies on your wireless adapters also supporting this feature. Different
manufacturers have developed different ways of converting plain text
and so interoperability is not guaranteed. If you are experiencing
difficulty, the Manual Hex Key method is supported by most vendors.
There are four methods available to generate the encryption keys:
■ Manual Key Entry - This method allows you to manually enter hex
keys. Virtually all manufacturers support this scheme. Enter a two digit
hexadecimal number in every box. Hexadecimal numbers are formed
from 0-9 and A-F.
■ 3Com Encryption String - This method is supported by 3Com Wireless
products. The string can contain any alphanumeric characters and
must be between 6 and 30 characters long. A single string will
automatically generate 4 unique keys for 64 or 128 bit WEP.
■ ASCII - This method is supported by some adapter cards running
under Windows XP. The string must be exactly 5 characters for 64 bit










