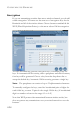
WIRELESS Wireless The Barricade also operates as a wireless-to-wired bridge, allowing wireless computers to access resources available on the wired LAN, and to access the Internet. To configure the Barricade as a wireless access point for wireless clients (either stationary or roaming), all you need to do is enable the wireless function, define the radio channel, the domain identifier, and the encryption options. Check Enable and click APPLY.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE Channel and SSID You must specify a common radio channel and SSID (Service Set ID) to be used by the Barricade Wireless Router and all of your wireless clients. Be sure you configure all of your clients to the same values. Parameter Description ESSID Extended Service Set ID. The ESSID must be the same on the Barricade and all of its wireless clients. Transmission Rate The default is Fully Automatic.
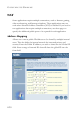
WIRELESS Parameter Description Basic Rate The highest rate specified will be the rate that the Barricade will use when transmitting broadcast/multicast and management frames. Available options are: All (1, 2, 5.5, and 11Mbps), and 1, 2Mbps (default is 1, 2Mbps). Channel The radio channel must be the same on the Barricade and all of your wireless clients. The Barricade will automatically assign itself a radio channel, or you may select one manually.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE Encryption If you are transmitting sensitive data across wireless channels, you should enable encryption. You must use the same set of encryption keys for the Barricade and all of the wireless clients. Choose between standard 64-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) or the more robust 128-bit encryption. You may automatically generate encryption keys or manually enter the keys. For automatic 64-bit security, enter a passphrase and click Generate, four keys will be generated.
WIRELESS MAC Address Filtering Client computers can be filtered using the unique MAC address of their IEEE 802.11 network card. To secure an access point using MAC address filtering, you must enter a list of allowed/denied client MAC addresses into the filtering table. (See “Finding the MAC address of a Network Card” on page 4-57.) Parameter Description Filtering Disable Disables MAC address filtering. Enable Enables MAC address filtering.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE NAT Some applications require multiple connections, such as Internet gaming, videoconferencing, and Internet telephony. These applications may not work when Network Address Translation (NAT) is enabled. If you need to run applications that require multiple connections, use these pages to specify the additional public ports to be opened for each application. Address Mapping Allows one or more public IP addresses to be shared by multiple internal users.
NAT Virtual Server If you configure the Barricade as a virtual server, remote users accessing services such as Web or FTP at your local site via public IP addresses can be automatically redirected to local servers configured with private IP addresses. In other words, depending on the requested service (TCP/UDP port number), the Barricade redirects the external service request to the appropriate server (located at another internal IP address).
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE For example, if you set Type/Public Port to TCP/80 (HTTP or Web) and the Private IP/Port to 192.168.2.2/80, then all HTTP requests from outside users will be transferred to 192.168.2.2 on port 80. Therefore, by just entering the IP Address provided by the ISP, Internet users can access the service they need at the local address to which you redirect them. The more common TCP service ports include: HTTP: 80, FTP: 21, Telnet: 23, and POP3: 110.
ROUTING SYSTEM Routing System These pages define routing related parameters, including static routes and RIP (Routing Information Protocol) parameters. Static Route Click Add to add a new static route to the list, or check the box of an already entered route and click Modify. Click Delete to remove an entry from the list. Parameter Description Index Check the box of the route you wish to delete or modify. Network Address Enter the IP address of the remote computer for which to set a static route.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE RIP Routing Information Protocol (RIP) sends routing-update messages at regular intervals and when the network topology changes. When a router receives a routing update that includes changes to an entry, it updates its routing table to reflect the new route. RIP routers maintain only the best route to a destination. After updating its routing table, the router immediately begins transmitting routing updates to inform other network routers of the change.
ROUTING SYSTEM Parameter Description Poison Reverse A way in which a router tells its neighbor routers that one of the routers is no longer connected. Authentication Required • None: No authentication. • Password: A password authentication key is included in the packet. If this does not match what is expected, the packet will be discarded. This method provides very little security as it is possible to learn the authentication key by watching RIP packets.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE Routing Table Parameter Description Flags Indicates the route status: C = Direct connection on the same subnet. S = Static route. R = RIP (Routing Information Protocol) assigned route. I = ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Redirect route. Network Address Destination IP address. Netmask The subnetwork associated with the destination. This is a template that identifies the address bits in the destination address used for routing to specific subnets.
FIREWALL Firewall The Barricade Router’s firewall inspects packets at the application layer, maintains TCP and UDP session information including time-outs and number of active sessions, and provides the ability to detect and prevent certain types of network attacks. Network attacks that deny access to a network device are called Denial-ofService (DoS) attacks. DoS attacks are aimed at devices and networks with a connection to the Internet.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE Access Control Access Control allows users to define the outgoing traffic permitted or not-permitted through the WAN interface. The default is to permit all outgoing traffic. The Barricade can also limit the access of hosts within the local area network (LAN). The MAC Filtering Table allows the Barricade to enter up to 32 MAC addresses that are not allowed access to the WAN port.
FIREWALL 1. Click Add PC on the Access Control screen. 2. Define the appropriate settings for client PC services (as shown on the following screen). 3. Click OK and then click APPLY to save your settings.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE URL Blocking The Barricade allows the user to block access to Web sites from a particular PC by entering either a full URL address or just a keyword. This feature can be used to protect children from accessing violent or pornographic Web sites.
FIREWALL Schedule Rule You may filter Internet access for local clients based on rules. Each access control rule may be activated at a scheduled time. Define the schedule on the Schedule Rule page, and apply the rule on the Access Control page. Follow steps to add schedule rule: 1. Click Add Schedule Rule. 2. Define the appropriate settings for a schedule rule (as shown on the following screen). 3. Click OK and then click APPLY to save your settings.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE Intrusion Detection 4-42
FIREWALL • Intrusion Detection Feature SPI and Anti-DoS firewall protection (Default: Enabled) — The Intrusion Detection Feature of the Barricade Router limits access for incoming traffic at the WAN port. When the SPI feature is turned on, all incoming packets will be blocked except for those types marked with a check in the Stateful Packet Inspection section. RIP Defect (Default: Enabled) — If an RIP request packet is not replied to by the router, it will stay in the input queue and not be released.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE Stateful Packet Inspection allows you to select different application types that are using dynamic port numbers. If you wish to use the Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) to block packets, click on the Yes radio button in the “Enable SPI and Anti-DoS firewall protection” field and then check the inspection type that you need, such as Packet Fragmentation, TCP Connection, UDP Session, FTP Service, H.323 Service, and TFTP Service.
FIREWALL • DoS Criteria and Port Scan Criteria Set up DoS and port scan criteria in the spaces provided (as shown below). Parameter Defaults Description Total incomplete TCP/UDP sessions HIGH 300 sessions Defines the rate of new unestablished sessions that will cause the software to start deleting half-open sessions. Total incomplete TCP/UDP sessions LOW 250 sessions Defines the rate of new unestablished sessions that will cause the software to stop deleting half-open sessions.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE DMZ If you have a client PC that cannot run an Internet application properly from behind the firewall, you can open the client up to unrestricted two-way Internet access. Enter the IP address of a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) host on this screen. Adding a client to the DMZ may expose your local network to a variety of security risks, so only use this option as a last resort.
SNMP SNMP Use the SNMP configuration screen to display and modify parameters for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). Community A computer attached to the network, called a Network Management Station (NMS), can be used to access this information. Access rights to the agent are controlled by community strings. To communicate with the Barricade, the NMS must first submit a valid community string for authentication.
CONFIGURING THE BARRICADE Trap Specify the IP address to notify an NMS that a significant event has occurred at an agent. When a trap condition occurs, the SNMP agent sends an SNMP trap message to any NMSs specified as the trap receivers. Parameter Description IP Address Traps are sent to this address when errors or specific events occur on the network. Community A community string (password) specified for trap management.
ADSL ADSL ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) is designed to deliver more bandwidth downstream (from the central office to the customer site) than upstream. This section is used to configure the ADSL operation type and shows the ADSL status. Parameters Parameter Operation Mode Address 3C etc. Description • Automatic • ETSI DTS/TM-06006 standard • G.992.1 standard Reserved.