Instruction Manual
Table Of Contents
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Procedures of Assembly/Disassembly
- Chapter 3 Board Introduction
- Chapter 4 H/W Information
- Chapter 5 BIOS Settings
- SATA Configuration
- W83627DHG Super IO Configuration
- Serial Port Console Redirection
- Intel(R) 82576 Gigabit Dual Port Network Connection
- N/A
- Configure Gigabit Ethernet device parameters
- Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection
- N/A
- Configure Gigabit Ethernet device parameters
- SATA Mode Selection
- Port 1
- Port 2
- CF card
- COM1 Configuration
- COM2 Configuration
- LAN by Pass Function
- Change Settings
- Serial Port
- Change Settings
- Device Mode
- Console Redirection
- Console Redirection Settings
- EMS
- EMS Settings
- Terminal Type
- Bits per second
- Data Bits
- Parity
- Stop Bits
- Flow Control
- NIC Configuration
- Blink LEDs (range 0-1
- Link Status
- NIC Configuration
- Blink LEDs (range 0-1
- Link Status
- SYS temperature
- CPU temperature
- CPU Fan Speed
- VCORE
- LAN1 ~ 8
- USB Configuration
- xHCI Mode
- EHCI1
- Setup Prompt Timeout
- Boot up NumLock State
- Boot Logo
- PXE Function
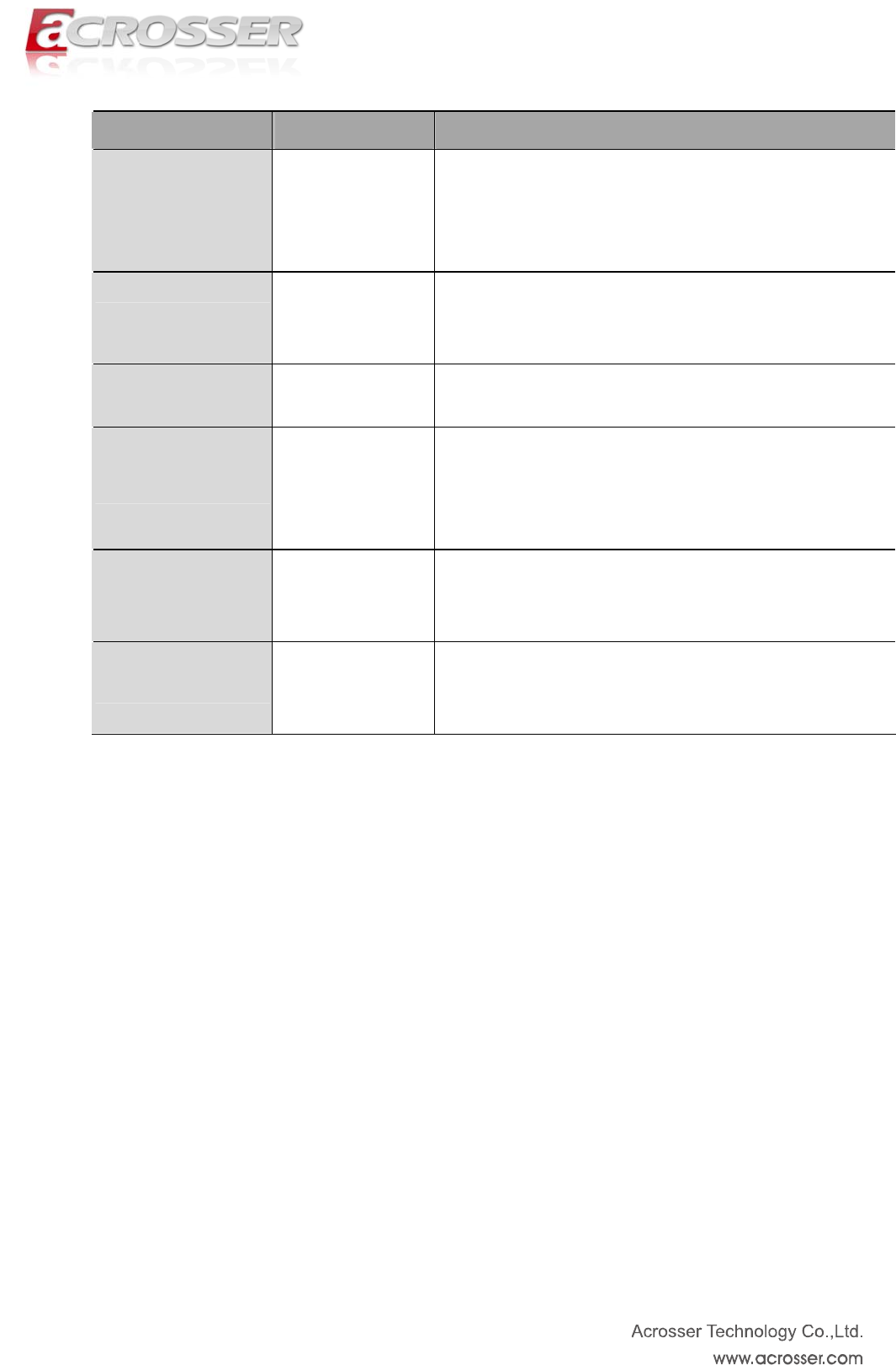
Option Choice Description
Terminal Type
VT100 / VT100+ /
VT-UTF8 / ANSI
Emulation: ANSI: Extended ASCII char set. VT100: ASCII
char set. VT100+: Extends VT100 to support color, function
keys, etc. VT-UTF8: Uses UTF8 encoding to map Unicode
chars onto 1 or more
Bits per second
9600 / 19200 /
38400 / 57600 /
115200
Selects serial port transmission speed. The speed must be
matched on the other side. Long or noisy lines may require
lower speeds.
Data Bits
7 / 8 Data Bits
Parity
None / Even / Odd /
Mark / Space
A parity bit can be sent with the data bits to detect some
transmission errors. Even: parity bit is 0 if the num of 1's in
the data bits is even. Odd: parity bit is 0 if num of 1's in the
data
Stop Bits
1 / 2
Stop bits indicate the end of a serial data packet. (A start bit
indicates the standard setting is 1 stop bit. Communication
with slow devices may require more than 1
Flow Control
None / Hardware
RTS/CTS
Flow control can prevent data loss from buffer overflow.
When sending data, if the receiving buffers are full, a 'stop'
signal can be sent to stop the data flow.
43










