User`s manual
24
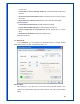
Fill the text box by following the rule below:
64-bit – Input 10-digit Hex values (in the “A-F”, “a-f, and “0-9” range) or 5-digit ASCII
characters (including “a-z” and “0-9”) as the encryption keys. For example: “0123456aef”
or “test1”
128-bit – Input 26-digit Hex values (in the “A-F”, “a-f, and “0-9” range) or 13-digit ASCII
characters (including “a-z” and “0-9”) as the encryption keys. For example:
“01234567890123456789abcdef” or “administrator”
3.3.3 802.1x Setting-Certification
The IEEE 802.1X specification describes a protocol that can be used for authenticating
both clients and servers on a network. The authentication algorithms and methods are those
provided by the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP), a method of authentication that has
been in use for a number of years on networks that provide Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
support as many Internet service providers and enterprises do.
When an AP acting as an authenticator detects a wireless station on the LAN, it sends
an EAP-Request for the user’s identity to the device. (EAP, or the Extensible Authentication
Protocol, is an authentication protocol that runs before network layer protocols transmit data
over the link) In turn, the device responds with its identity, and the AP relays this identity to an
authentication server, which is typically an external RADIUS server.
[An example for MD5 Authentication]