User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Figures
- Preface
- Section I
- Basic Operations
- Chapter 1
- Starting a Web Browser Management Session
- Chapter 2
- Basic Switch Parameters
- Chapter 3
- Enhanced Stacking
- Chapter 4
- SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c Community Strings
- Chapter 5
- Port Parameters
- Chapter 6
- MAC Address Table
- Chapter 7
- Static Port Trunks
- Chapter 8
- Port Mirroring
- Section II
- Advanced Operations
- Chapter 9
- File System
- Chapter 10
- File Downloads and Uploads
- Chapter 11
- Event Log and Syslog Servers
- Chapter 12
- Classifiers
- Chapter 13
- Access Control Lists
- Chapter 14
- Quality of Service
- Chapter 15
- Class of Service
- Chapter 16
- IGMP Snooping
- Chapter 17
- Denial of Service Defense
- Chapter 18
- Power Over Ethernet
- Section III
- SNMPv3 Operations
- Chapter 19
- SNMPv3
- Enabling the SNMP Protocol
- Configuring the SNMPv3 User Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 View Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Access Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 SecurityToGroup Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Notify Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Target Address Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Target Parameters Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Community Table
- Displaying SNMPv3 Tables
- Section IV
- Spanning Tree Protocols
- Chapter 20
- Spanning Tree, Rapid Spanning Tree, and Multiple Spanning Tree Protocols
- Section V
- Virtual LANs
- Chapter 21
- Port-based and Tagged Virtual LANs
- Chapter 22
- GARP VLAN Registration Protocol
- Chapter 23
- Protected Ports VLANs
- Section VI
- Port Security
- Chapter 24
- MAC Address-based Port Security
- Chapter 25
- 802.1x Port-based Network Access Control
- Section VII
- Management Security
- Chapter 26
- Encryption Keys, PKI, and SSL
- Chapter 27
- Secure Shell Protocol
- Chapter 28
- TACACS+ and RADIUS Authentication Protocols
- Chapter 29
- Management Access Control List
- Index
Chapter 20: Spanning Tree, Rapid Spanning Tree, and Multiple Spanning Tree Protocols
288 Section IV: Spanning Tree Protocols
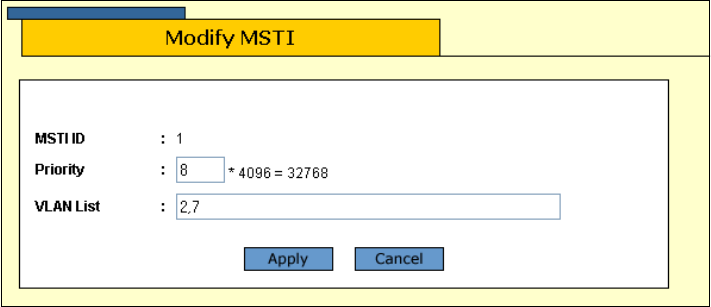
The Modify MSTI window is shown in Figure 98.
Figure 98. Modify MSTI Window
c. In the Priority field, enter a new MSTI Priority value. This
parameter is used in selecting a regional root for the MSTI. The
range is 0 (zero) to 61,440 in increments of 4,096, with 0 being the
highest priority. The default is 0.There are sixteen increments. You
specify the increment representing the desired bridge priority
value. The increments are shown in Table 7 on page 275.
d. In the VLAN List field, modify the list of VIDs of the VLANs to be
associated with this MSTI. You can add more VLANs or remove
VLANs. You can specify more than one VID at a time (e.g., 2,4,7).
If you remove a VLAN, the VLAN will be associated with CIST.
e. Click Apply.
f. Repeat this procedure to modify more MSTI IDs.
4. To delete an MSTI ID, do the following:
a. In the CIST/MSTI Table section of the menu, click the circle next to
the MSTI ID you want to delete. You can select only one MSTI ID
at a time.
b. Click Remove.
A confirmation prompt is displayed.
c. Click OK to delete the MSTI or Cancel to cancel the procedure.
If you select OK, the MSTI is deleted and VLANs associated with it
are returned to CIST, which has an ID of 0.
5. To permanently save the changes, select the Save Config menu
selection.










