User guide
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Preface
- Section I
- Basic Operations
- Chapter 1
- Basic Switch Parameters
- Configuring the Switch’s Name, Location, and Contact
- Changing the Manager and Operator Passwords
- Setting the System Date and Time
- Rebooting a Switch
- Pinging a Remote System
- Returning the AT-S63 Management Software to the Factory Default Values
- Displaying the IP Address of the Local Interface
- Displaying System Information
- Chapter 2
- Port Parameters
- Chapter 3
- Enhanced Stacking
- Chapter 4
- SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c
- Chapter 5
- MAC Address Table
- Chapter 6
- Static Port Trunks
- Chapter 7
- Port Mirroring
- Section II
- Advanced Operations
- Chapter 8
- File System
- Chapter 9
- File Downloads and Uploads
- Chapter 10
- Event Logs and Syslog Client
- Chapter 11
- Classifiers
- Chapter 12
- Access Control Lists
- Chapter 13
- Class of Service
- Chapter 14
- Quality of Service
- Chapter 15
- Denial of Service Defenses
- Chapter 16
- IGMP Snooping
- Section III
- SNMPv3
- Chapter 17
- SNMPv3
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Protocol
- Enabling or Disabling SNMP Management
- Configuring the SNMPv3 User Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 View Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Access Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 SecurityToGroup Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Notify Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Target Address Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Target Parameters Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Community Table
- Displaying SNMPv3 Tables
- Section IV
- Spanning Tree Protocols
- Chapter 18
- Spanning Tree and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocols
- Chapter 19
- Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
- Section V
- Virtual LANs
- Chapter 20
- Port-based and Tagged VLANs
- Chapter 21
- GARP VLAN Registration Protocol
- Section VI
- Port Security
- Chapter 22
- MAC Address-based Port Security
- Chapter 23
- 802.1x Port-based Network Access Control
- Section VII
- Management Security
- Chapter 24
- Encryption Keys, PKI, and SSL
- Chapter 25
- Secure Shell (SSH)
- Chapter 26
- TACACS+ and RADIUS Protocols
- Chapter 27
- Management Access Control List
- Index
Chapter 18: Spanning Tree and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocols
278 Section IV: Spanning Tree Protocols
Bridge Hello Time
The time interval between generating and sending configuration
messages by the bridge. This parameter can be from 1 to 10 seconds.
The default is 2 seconds.
Bridge Forwarding Delay
The waiting period in seconds before a bridge changes to a new state,
for example, becomes the new root bridge after the topology changes.
If the bridge transitions too soon, not all links may have yet adapted to
the change, resulting in network loops. The range is 4 to 30 seconds.
The default is 15 seconds.
Bridge Max Age
The length of time after which stored bridge protocol data units
(BPDUs) are deleted by the bridge. All bridges in a bridged LAN use
this aging time to test the age of stored configuration messages called
bridge protocol data units (BPDUs). For example, if you use the default
value 20, all bridges delete current configuration messages after 20
seconds. This parameter can be from 6 to 40 seconds.
In selecting a value for maximum age, the following rules must be
observed:
MaxAge must be greater than (2 x (HelloTime + 1))
MaxAge must be less than (2 x (ForwardingDelay - 1))
Note
The aging time for BPDUs is different from the aging time used by
the MAC address table.
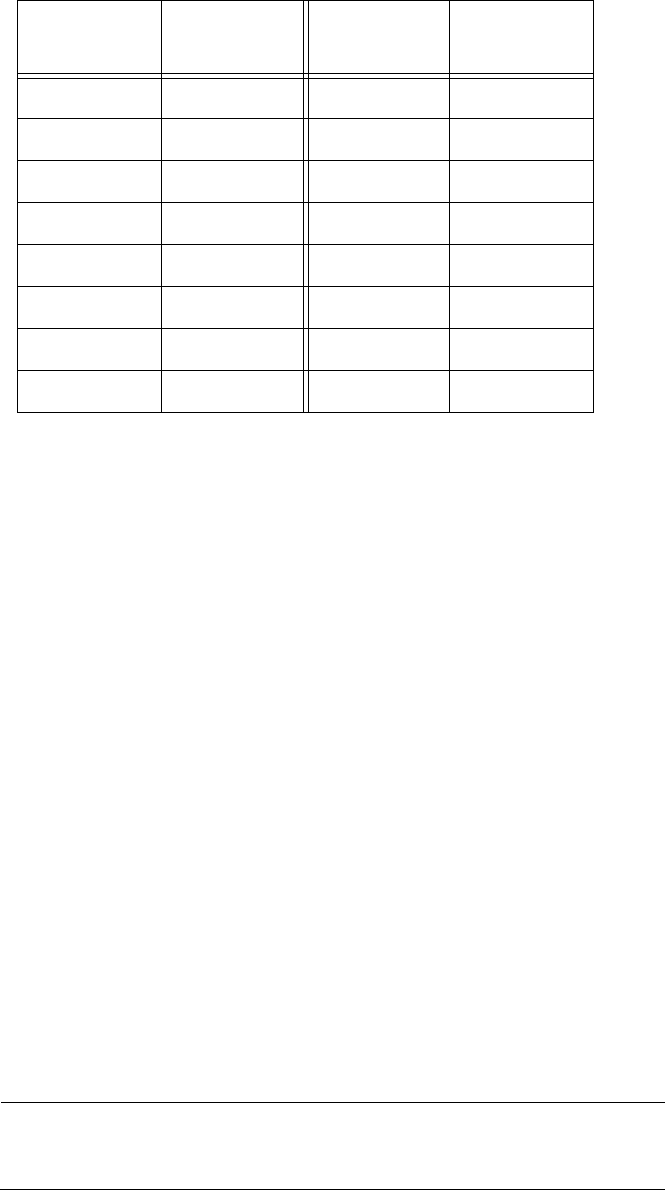
Table 5. Bridge Priority Value Increments
Increment
Bridge
Priority
Increment
Bridge
Priority
0 0 8 32768
1 4096 9 36864
2 8192 10 40960
3 12288 11 45056
4 16384 12 49152
5 20480 13 53248
6 24576 14 57344
7 28672 15 61440










