User guide
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Preface
- Section I
- Basic Operations
- Chapter 1
- Basic Switch Parameters
- Configuring the Switch’s Name, Location, and Contact
- Changing the Manager and Operator Passwords
- Setting the System Date and Time
- Rebooting a Switch
- Pinging a Remote System
- Returning the AT-S63 Management Software to the Factory Default Values
- Displaying the IP Address of the Local Interface
- Displaying System Information
- Chapter 2
- Port Parameters
- Chapter 3
- Enhanced Stacking
- Chapter 4
- SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c
- Chapter 5
- MAC Address Table
- Chapter 6
- Static Port Trunks
- Chapter 7
- Port Mirroring
- Section II
- Advanced Operations
- Chapter 8
- File System
- Chapter 9
- File Downloads and Uploads
- Chapter 10
- Event Logs and Syslog Client
- Chapter 11
- Classifiers
- Chapter 12
- Access Control Lists
- Chapter 13
- Class of Service
- Chapter 14
- Quality of Service
- Chapter 15
- Denial of Service Defenses
- Chapter 16
- IGMP Snooping
- Section III
- SNMPv3
- Chapter 17
- SNMPv3
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Protocol
- Enabling or Disabling SNMP Management
- Configuring the SNMPv3 User Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 View Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Access Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 SecurityToGroup Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Notify Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Target Address Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Target Parameters Table
- Configuring the SNMPv3 Community Table
- Displaying SNMPv3 Tables
- Section IV
- Spanning Tree Protocols
- Chapter 18
- Spanning Tree and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocols
- Chapter 19
- Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
- Section V
- Virtual LANs
- Chapter 20
- Port-based and Tagged VLANs
- Chapter 21
- GARP VLAN Registration Protocol
- Section VI
- Port Security
- Chapter 22
- MAC Address-based Port Security
- Chapter 23
- 802.1x Port-based Network Access Control
- Section VII
- Management Security
- Chapter 24
- Encryption Keys, PKI, and SSL
- Chapter 25
- Secure Shell (SSH)
- Chapter 26
- TACACS+ and RADIUS Protocols
- Chapter 27
- Management Access Control List
- Index
AT-S63 Management Software Web Browser User’s Guide
Section IV: Spanning Tree Protocols 311
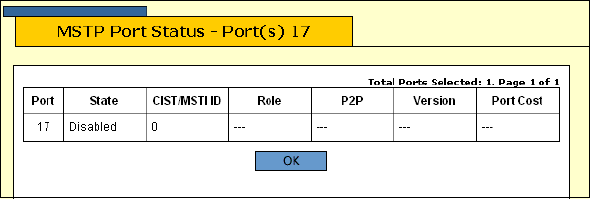
The MSTP Port Status - Port(s) page is shown in Figure 127.
Figure 127. MSTP Port Status - Port(s) Page
The MSTP Port Status page displays a table with the following
columns of information:
Port
The port number.
State
The MSTP state of the port. The possible states are:
Discarding - The port is discarding received packets and is not
submitting forwarded packets for transmission.
Learning - The port is enabled for receiving, but not forwarding
packets.
Forwarding - Normal operation.
Disabled - The port has not established a link with its end node.
Role
The MSTP role of the port. The possible roles are:
Root - The port that is connected to the root switch, directly or through
other switches, with the least path cost.
Alternate - The port offers an alternate path in the direction of the root
switch.
Backup - The port on a designated switch that provides a backup for
the path provided by the designated port.
Designated - The port on the designated switch for a LAN that has the
least cost path to the root switch. This port connects the LAN to the
root switch.
Master - Similar to the root port. When the port is a boundary port, the
MSTI port roles follow the CIST port roles. The MSTI port role is called
“master” when the CIST role is “root.”










