Manual
Table Of Contents
- Table 1-1, DSM3 Series Model Specifications
- Table 2-1, LEDs and Indications
- Table 3-1, Modem Community String Parameters — DOCSIS 2.0 (IPv4) Method
- Table 3-2, Modem Community String Parameters — DOCSIS 2.0+IPv6 Method
- Table 3-3, Trap Destination Addresses — DOCSIS 2.0 (IPv4) Method
- Table 3-4, Trap Destination Addresses — DOCSIS 2.0+IPv6 Method
- Table 3-5, Default atidoc.cfg Download Settings
- Table 3-6, Communications Parameters
- Table 4-1, DSM3 Series Communications Module Security Levels
- Table 4-3, Time Offset Values and Location Reference (offset +/- GMT)
- Table 5-1, Modem Firmware Upgrade SNMP Parameters
- Table 5-2, SNMP Parameters
- Table 5-3, DOCSIS Configurations File Values
- Table 6-1, SCTE-HMS MIB Files
- Table 6-2, Binary to Hex Conversions for Alarm Settings
- Table 6-3, Recommended Settings for DSM3 Series Analog Alarms
- Table 6-4, Recommended Settings for Discrete Alarms
- Table 6-5, DSM Alarm Setting Paramters
- Table 6-6, Status of Alarm Setting Download Parameters
- Table 6-7, SNMP Alarm Trap Varbinds and Explanations
- Table 6-8, Power Alarms: Classifications, Causes and Corrections
- Table 6-9, Battery Alarms: Classifications, Causes and Corrections
- Table 6-9, Alpha MIB Hierarchy
- Table 6-10, Alpha MIBs Examples
- Table 7-1, Tamper (TPR) Switch Specifications
- Table 7-2, ENV Connector and Pin Descriptions
- Table 7-3, I/O Port Specifications
- Table 7-4, I/O Port: Generic Device Specifications
- Table 7-5, LA-P-SM Monitoring Values
- Table 7-6, I/O Port: Heater Mat Control Specifications
- Table 7-7, Heater Mat OIDs and Functionality
- Table 7-8, Heater Mat MIB Reports
- Table 7-9, Generator Monitoring Values
- Table 9-1,SCTE-HMS Property Table
- Table 9-2, Rx/Tx Power LED Color Ranges
- Table 13-1, Single IP Mode versus Dual IP Mode
- Table 13-2, Enabling Dual IP mode
- Table 13-3, CPE Communications Module IP Settings
- Table 13-4, Available Download Options
- 1.0 Introduction
- 2.0 Overview
- 3.0 Network Configuration
- 3.1 Provisioning the DHCP Server with the MAC Addresses
- 3.2 Establishing IP Connectivity
- 3.3 The DOCSIS Configuration File
- 3.3.8 Changing Default atidoc03.cfg Download Settings
- 3.3.7 Proprietary Configuration File ‘atidoc03.cfg’
- 3.3.6 Sample DOCSIS Configuration File Entries — DOCSIS 2.0+IPv6
- 3.3.5 Sample DOCSIS Configuration File Entries — DOCSIS 2.0 (IPv4)
- 3.3.4 Setting SNMP Trap Destination Addresses — DOCSIS 2.0+IPv6 Method
- 3.3.3 Setting SNMP Trap Destination Addresses — DOCSIS 2.0 (IPv4) Method
- 3.3.2 Setting Modem Community Strings — DOCSIS 2.0+IPv6 Method
- 3.4 Setting Communication Options
- 4.0 Web Interface
- 4.1 Local Web Server Access
- 4.2 Remote Web Server Access
- 4.3 Navigating the Web Page
- 4.4 Verifying Communication Parameters
- 4.5 Verifying Power Supply and Battery Parameters
- 4.6 Remote Self Tests via the Web Page
- 4.7 Viewing HMS Alarm Status via the Web Page
- 4.8 Setting the I/O Controller via the Web Page
- 4.9 Viewing and Configuring Power Supply settings via the Web Page
- 4.10 Viewing and Configuring Generator Settings via the Web Page
- 4.11 Tools Menu – Constellation and Microreflections
- 4.12 Viewing AlphaApps Information via the Web Page
- 4.13 Battery Management
- 4.14 Viewing Power Supply Event and Configuration Logs
- 4.15 Battery Event Log
- 4.16 Viewing the Modem Event Log via the Web Page
- 5.0 Upgrading Firmware
- 6.0 Data Management
- 7.0 Installation
- 7.1 Verifying Power Supply Device Address
- 7.2 Installation / Replacement Procedure in XM3 Power Supplies
- 7.3 DSM3x LEDs and Connections
- 7.4 DSM3 LEDs and Connections
- 7.5 DPM LEDs and Connections
- 7.6 Connecting the RF Drop
- 7.7 Front Panel Connections
- 7.8 I/O Connections (TPR, ENV)
- 7.8.1 Tamper (TPR) Switch Interface
- 7.8.2 I/O Port Interface
- 7.8.3 Configuring I/O Port Connections
- 7.8.4 I/O Port: Generic Device
- 7.8.5 Connecting a Generic I/O Device
- 7.8.6 Configuring and Monitoring a Generic I/O Device
- 7.8.7 I/O Port: Lightning Arrestor (LA-P-SM)
- 7.8.8 Lightning Arrestor (LA-P-SM) Installation
- 7.8.9 Configuring the LA-P-SM
- 7.8.10 I/O Port: Heater Mat Control
- 7.8.11 Connecting the Battery Heater Mat Controller, continued
- 7.8.12 Configuring the Battery Heater Mat Controller
- 7.8.14 Configuring and Monitoring the DC Emergency Generator
- 8.0 Battery Sense Wire Kits
- 9.0 Start Up and Verification
- 10.0 Alpha MIB Parameters
- 11.0 Specifications
- 12.0 Glossary
- 13.0 Dual IP Mode (Addendum)
- 13.1 Overview
- 13.2 Web Comparison, Single IP Mode/Dual IP Mode
- 13.3 Configuring Dual IP Mode
- 13.3.3 Specifying atidoc03.cfg name and location via DHCP Tags
- 13.3.2 Changing Default atidoc03.cfg Download Settings in Dual IP Mode
- 13.3.1 atidoc03.cfg in Dual IP Mode
- 13.4 Dual IP SNMP Community Strings
- 13.5 Security in Dual IP Mode
- Fig. 1-1, AlphaNet DSM3x
- Fig. 1-2, AlphaNet DSM3
- Fig. 1-3, AlphaNet DPM
- Fig. 1-4, Side view, AlphaNet DSM3 Series
- Fig. 2-1, Representative System Arrangement
- Fig. 3-1, Locations of MAC Address Labels
- Fig. 3-2, Sample DOCSIS Configuration File — DOCSIS 2.0 (IPv4)
- Fig. 3-3, Sample DOCSIS Configuration File — DOCSIS 2.0+IPv6
- Fig. 4-1, DSM3 Series Web Page
- Fig. 4-2, Local Area Connection Properties Screen, Windows XP
- Fig. 4-3, Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties Screen, Windows XP
- Fig. 4-4, Local Area Connection Properties Screen, Windows 7
- Fig. 4-5, Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties Screen, Windows 7
- Fig. 4-6, Web Server Home Page
- Fig. 4-7, DSM3 Series Navigation Bar Items
- Fig. 4-8, Communication Parameters
- Fig. 4-9, Advanced Communication Parameters
- Fig. 4-10, Power Supply and Battery Parameters
- Fig. 4-11, Location of Start Test Button for Self Test
- Fig. 4-12, HMS Alarm Configuration
- Fig. 4-13, Advanced I/O Controller Status Screen
- Fig. 4-14, Advanced Power Supply Settings Screen
- Fig. 4-15, Advanced Generator Status Screen
- Fig. 4-16, QAM Constellation Tool
- Fig. 4-17, Normal - (Good Quality) and Individual Cell Characteristics
- Fig. 4-18, Fuzzy (Low CNR and/or Low MER) and Individual Cell Characteristics
- Fig. 4-19, Doughnuts (Coherent Interference) and Individual Cell Characteristics
- Fig. 4-20, Gaussian Noise and Individual Cell Characteristics
- Fig. 4-21, Rectangular vs. Square (I-Q Imbalance) and Entire Constellation Shape
- Fig. 4-22, Corners Squeezed to Center (Gain Compression) and Entire Constellation Shape
- Fig. 4-23, Circular Smear (Phase Noise) and Entire Constellation Shape
- Fig. 4-24, Twisted or Skewed (Quadrature Distortion) and Entire Constellation Shape
- Fig. 4-25, Microreflections Tool
- Fig. 4-26, Alpha Apps and Utility Status Parameters
- Fig. 4-27, Battery Management
- Fig. 4-28, Battery Model Selection
- Fig. 4-29, DSM3 System Log
- Fig. 4-30, Power Supply Event Log
- Fig. 4-31, Power Supply Configuration Log
- Fig. 4-33, Docsdev Event Log Screen
- Fig. 6-1, Sample Raw SNMP Alarm Trap
- Fig. 6-2, Sample Translated SNMP Alarm Trap
- Fig. 7-1, Captive Screw Locations
- Fig. 7-3, Connecting the Communications Module to the Inverter Module
- Fig. 7-2, The 18-pin Connector
- Fig. 7-4, DSM3x LEDs and Connectors
- Fig. 7-5, DSM3 LEDs and Connectors
- Fig. 7-6, DPM LEDs and Connectors
- Fig. 7-7, Connecting the RF Drop
- Fig. 7-8, System Interconnection Diagram
- Fig. 7-9, I/O (ENV) and Tamper Switch Interface (TPR) Connection Locations
- Fig. 8-1, 36V System, Single String
- Fig. 8-2, 36V System, Dual String
- Fig. 9-1, XM3 Smart Display Screens
- Fig. 9-2, Communications Section - General Page
- Fig. 9-3, Power Supply Section - General Page
- Fig. 9-4, LED Functionality and Indications
- Fig. 9-5, DSM3 Series Web Page, RF Power Level Indicators
- Fig. 13-1, Simplified Block Diagram Single IP Mode
- Fig 13-2, Simplified Block Diagram Dual IP Mode
- Fig. 13-3, Single IP DSM3 Series Web Page
- Fig. 13-4, Dual IP DSM3 Series Web Page
- Fig. 13-5, Dual IP Configuration Settings for DSM3 Web Server Communications Page
- Fig. 13-6, Dual IP Parameters for DSM3 Web Server General Page
14
745-814-B11-001, Rev. C (03/2014)
3.0 Network Conguration
3.2 Establishing IP Connectivity
The DSM3 Series supports the CableLabs DOCSIS 2.0+IPv6 implementation. The main benet of
IPv6 is its expanded addressing capability, increasing the address space from 32 to 128 bits, providing
virtually unlimited number of networks and systems. The DSM3 Series determines the IP provisioning
mode via the CableLabs SNMP MIB parameter docsIf3CmMdCfgIpProvMode (SNMP OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1
.4491.2.1.20.1.31.1.1). The DSM3 Series will support the following congurable IP Provisioning Mode
Override policies:
• Honor MDD: The cable modem of the DSM3 Series unit will acquire an IPv6 or IPv4 address as
directed by the MAC Domain Descriptor (MDD) message for provisioning and operation.
• IPv4 only: The cable modem of the DSM3 Series unit will acquire a single IPv4 address for the CM
management stack, overriding the TLVs in the MDD message.
• IPv6 only: The cable modem of the DSM3 Series unit will acquire a single IPv6 address for the CM
management stack, overriding the TLVs in the MDD message.
3.3 The DOCSIS Conguration File
A cable modem’s DOCSIS Conguration File is a type-length-value (TLV) le that contains important
operational parameters as dened by the DOCSIS standards. It provides certain settings for the cable
modem. In addition to standard entries, settings in the DOCSIS Conguration File should include the
modem’s community strings and if an upgrade is necessary, rmware upgrade parameters. Place the
Conguration File in the TFTP root directory.
The DSM3 Series cable modem interface can support both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes. The
required DOCSIS Conguration File operational parameters will differ depending on company policies,
cable modem rmware versions and IP addressing schemes. The following DOCSIS Conguration File
details listed in this manual are general guidelines. Please consult the published DOCSIS Specication
resources (CableLabs) for additional DOCSIS Conguration File details and guidelines.
To build a DOCSIS Conguration File, use a DOCSIS TLV editor program.
See the example Conguration Files in Sections 3.3.5 and 3.3.6.
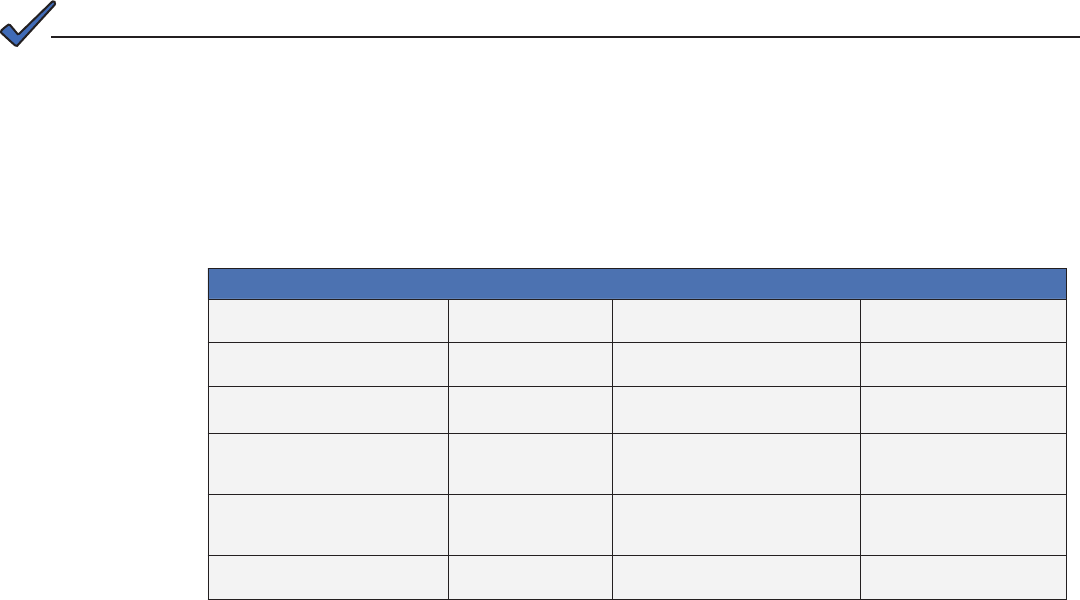
3.3.1 Setting Modem Community Strings — DOCSIS 2.0 (IPv4) Method
Set the modem community strings with the DOCSIS Conguration File by including the following
SNMP parameters:
The modem community strings should be set in the DOCSIS Conguration File. Failure to set community strings
will result in a less secure system. For automatically updating modem rmware with the DOCSIS Conguration File,
see Section 5.1, Upgrading DSM3 Series Modem Firmware.
NOTE:
MIB Parameter Object ID Description Value
docsDevNmAccessIp 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.2.x The IP address (or subnet) of the network
management station
e.g. 10.20.30.0
docsDevNmAccessIpMask 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.3.x The IP subnet mask of the network
management stations
e.g. 255.255.255.0
docsDevNmAccessCommunity 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.4.x The community string matched to this IP
address net mask entry
alphanumeric string
docsDevNmAccessControl 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.5.x The level of access granted 1= none
2= read only
3= read/write
docsDevNmAccessInterfaces 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.6.x Species the set of interfaces from which
requests from this NMS will be accepted
0x40 : Cable interface (typical)
0x80 : Ethernet interface
0xC0 or 0x00 : Both interfaces
docsDevNmAccessStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.69.1.2.1.7.x Controls and reects the status of rows in
this table
4
Table 3-1, Modem Community String Parameters — DOCSIS 2.0 (IPv4) Method
Note: X denotes the index of the SNMP entry










