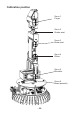
Instructions Circuit Diagram
- 34 -
7.5. Open a port – Linux
Linux handles the USB serial adaptor like a normal comport. The installation of
the D2XX driver from FTDI would not be as simple as that under Linux and the
normal virtual comport (VCP) drivers are included anyway in the current Linux
kernels. It works almost the same as under Windows. You just need to nd out
the name of the Robot Arm USB interface and make sure that the USB port
is not unplugged from the PC as long as the connection is open (otherwise
you might have to re-start the RobotLoader to re-connect). Under Linux the
names of the virtual comports are “/dev/ttyUSBx“, x being a number e.g. “/dev/
ttyUSB0“ or “/dev/ttyUSB1“. The names of the normal comports under Linux
are “/dev/ttyS0“, „/dev/tty- S1“ etc.. They also show up in the port list as far as
they exist.
The RobotLoader remembers - if there are several ports - which port you have
used last time and selects this port automatically when you start the program
(in general, most of the settings and selections are maintained).
Now you can click on the button “Connect“! The RobotLoader will open the
port and test if the communication with the bootloader on the robot is working.
The black eld “Status” on the bottom should show the message
“Connected to: Robot Arm ...” or similiar together with an information about the
currently measured voltage. If not, just try again! If it still doesn’t work, there is
a mistake! Switch the robot off immediately and start searching for the error.
If the voltage is too low, a warning is displayed. You should immediately
charge the accumulators (preferably even earlier when the voltage drops
below 4.0V)!
WARNING!
If the voltage drops below < 4,4 V, a warning is displayed.
The maximum voltage that the RobotLoader is able to measure, is 5.1 V!