User`s manual
ARTURIA – MOOG MODULAR V 2.6 – USER’S MANUAL 101
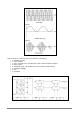
Triangle waveform
• The sinusoid is the purest waveform of them all. It is composed of a single
fundamental harmonic and produces a very “damper” sound (the tonality of a telephone
is sinusoid). It will be used to reinforce the low frequencies of a bass sound or as a
frequency modulator in order to create harmonics that do not exist in the original
waveforms.
Sinusoid waveform
A frequency modulation (FM) can be created between 2 oscillators by connecting the audio
output from a first sinusoidal oscillator to the modulation input of a second oscillator. On the
Moog Modular V, if you turn the modulation rate ring, you will obtain a sound richer in
harmonics. If you introduce a square or sawtooth signal, the result can be quickly distorted…
but interesting for inharmonic sonorities like bell sounds or special effects for example.
Frequency Modulation
The synchronization of an oscillator on another brings about complex waveforms. If, for
example, you synchronize oscillator2 on oscillator1, oscillator2 will restart another period each
time the first oscillator accomplishes a complete period, even if oscillator2 has not completed a
full period (which signifies that it is not tuned to the same tonality.) The higher you tune
oscillator2, the more you will obtain composite waveforms.