User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Reference for the Business Policy Switch 2000 Command Line Interface
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Preface
- Chapter 1: CLI Basics
- Stacking compatibility
- Software version 2.0 compatibility with BayStack 450 switches
- New features
- CLI command modes
- Port numbering
- IP notation
- Accessing the CLI
- Setting the CLI password
- Getting help
- Basic navigation
- Managing basic system information
- Managing MAC address forwarding database table
- Displaying and setting stack operational mode
- Chapter 2: General CLI commands
- Setting the terminal
- Pinging
- Automatically loading configuration file
- Assigning and clearing IP addresses
- Assigning and clearing IP addresses for specific units
- Setting Telnet access
- Setting server for Web-based management
- Setting boot parameters
- Setting TFTP parameters
- Upgrading software
- Displaying interfaces
- Setting SNMP parameters
- Setting the system event log
- Displaying port statistics
- Enabling or disabling a port
- Naming ports
- Setting port speed
- Enabling Autopology
- Enabling flow control
- Enabling rate-limiting
- Chapter 3: Security
- Using the IP manager list
- Using MAC address security
- show mac-security command
- show mac-security mac-da-filter command
- mac-security command
- mac-security mac-address-table address command
- mac-security security-list command
- no mac-security command
- no mac-security mac-address-table command
- no mac-security security-list command
- mac-security command for specific ports
- mac-security mac-da-filter command
- Using EAPOL-based security
- Using RADIUS authentication
- Chapter 4: Spanning Tree, MLT, and Port-Mirroring
- Using spanning tree
- show spanning-tree command
- spanning-tree stp create command by STG
- spanning-tree stp delete command by STG
- spanning-tree stp enable command by STG
- spanning-tree stp disable command by STG
- spanning-tree command by STG
- default spanning-tree command by STG
- spanning-tree add-vlan command
- spanning-tree remove-vlan command
- spanning-tree command by port
- default spanning-tree command by port
- no spanning-tree command by port
- Using MLT
- Using port-mirroring
- Using spanning tree
- Chapter 5: VLANs and IGMP
- Increased VLAN support
- Configuring and displaying VLANs
- show vlan interface info command
- show vlan interface vids command
- vlan mgmt command
- default vlan mgmt command
- vlan create command
- vlan delete command
- no vlan command
- vlan name command
- auto-pvid command
- no auto-pvid command
- vlan ports command
- vlan members command
- show vlan mac-address command
- vlan mac-address command
- no vlan mac-address command
- Displaying multicast membership
- Using IGMP snooping
- Chapter 6: Policy-enabled networks and QoS
- Displaying QoS parameters
- Resetting
- Configuring COPS
- Configuring QoS interface groups
- Configuring DSCP and 802.1p and queue associations
- Configuring QoS filters and filter groups
- Configuring QoS actions
- Configuring QoS meters
- Configuring QoS shapers
- Gathering QoS statistics
- Configuring QoS policies
- Reordering packets
- Appendix A: Command List
- Index
Chapter 6 Policy-enabled networks and QoS 199
Reference for the Business Policy Switch 2000 Command Line Interface
qos ip-filter command
The qos ip-filter command adds or deletes IP filters. The syntax for the qos
ip-filter
command is:
qos ip-filter <fid> {create [src-ip <src-ip-info>] [dst-ip
<dst-ip-info>] [ds-field <dscp>] [protocol <protocoltype>]
[src-port <port>] [dst-port <port>]|delete}
The qos ip-filter command is in the config command mode.
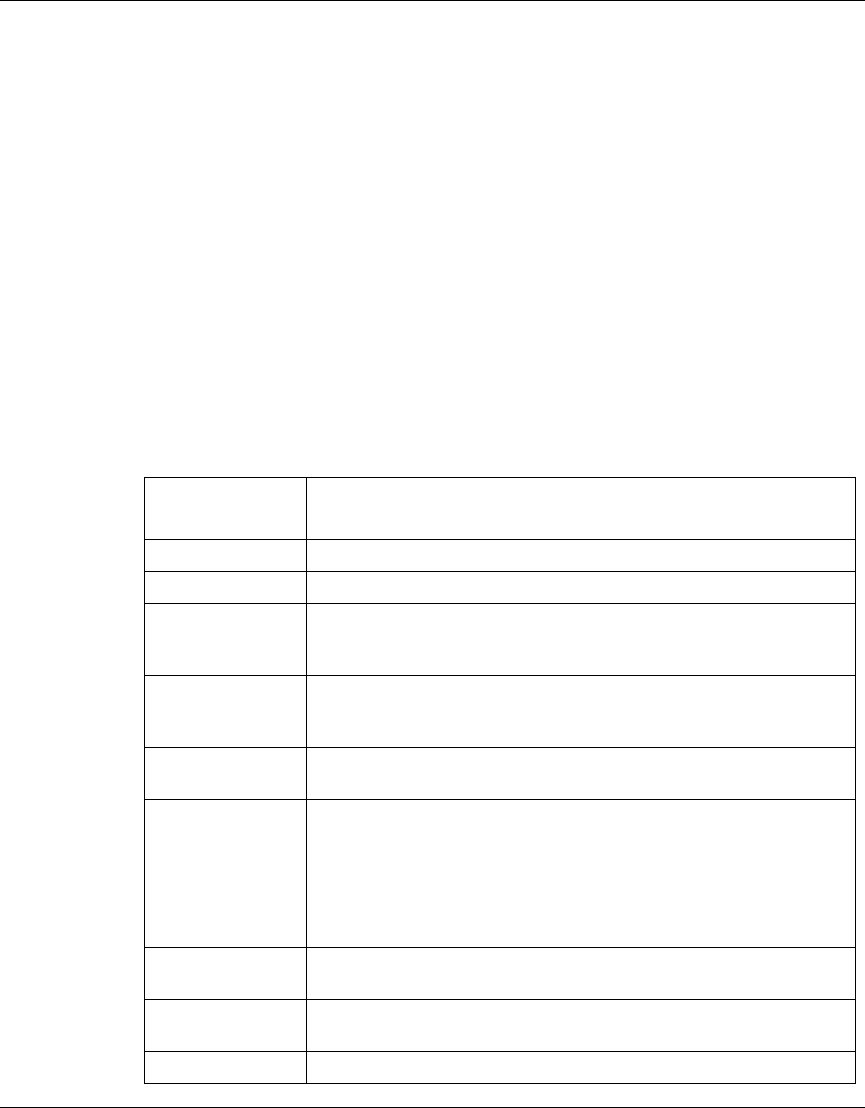
Table 116 describes the parameters and variables for the
qos ip-filter
command.
Table 116 qos ip-filter command parameters and variables
Parameters and
variables
Description
<fid> Enter an integer to specify the filter ID.
create Defines a new IP filter with the specified filter ID.
src-ip <src-ip-info> Enter the source IP address and mask in the form of a.b.c.d/x or
a.b.c.d x.x.x.x.
Default is 0.0.0.0.
dst-ip <dst-ip-info> Enter the destination IP address and mask in the form of a.b.c.d/x or
a.b.c.d x.x.x.x.
Default is 0.0.0.0.
ds-field <dscp> Enter 6-bit DSCP value; range is 0 to 63.
Default is ignore.
protocol
<protocoltype>
Enter the protocol type:
• ignore
• icmp
• tcp
• udp
Default is ignore.
src-port <port> Enter TCP/UDP source port value.
Default is ignore.
dst-port <port> Enter TCP/UDP destination port value.
Default is ignore.
delete Deletes the IP filter with the specified filter ID.










