Datasheet
ST72334J/N, ST72314J/N, ST72124J
85/153
14.5 SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE (SCI)
14.5.1 Introduction
The Serial Communications Interface (SCI) offers
a flexible means of full-duplex data exchange with
external equipment requiring an industry standard
NRZ asynchronous
serial data format. The SCI offers a very wide
range of baud rates using two baud rate generator
systems.
14.5.2 Main Features
■ Full duplex, asynchronous communications
■ NRZ standard format (Mark/Space)
■ Dual baud rate generator systems
■ Independently programmable transmit and
receive baud rates up to 250K baud using
conventional baud rate generator and up to
500K baud using the extended baud rate
generator.
■ Programmable data word length (8 or 9 bits)
■ Receive buffer full, Transmit buffer empty and
End of Transmission flags
■ Two receiver wake-up modes:
– Address bit (MSB)
– Idle line
■ Muting function for multiprocessor configurations
■ LIN compatible (if MCU clock frequency
tolerance
≤2%)
■ Separate enable bits for Transmitter and
Receiver
■ Three error detection flags:
– Overrun error
– Noise error
– Frame error
■ Five interrupt sources with flags:
– Transmit data register empty
– Transmission complete
– Receive data register full
– Idle line received
– Overrun error detected
14.5.3 General Description
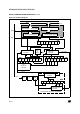
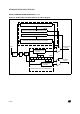
The interface is externally connected to another
device by two pins (see Figure 2.):
– TDO: Transmit Data Output. When the transmit-
ter is disabled, the output pin returns to its I/O
port configuration. When the transmitter is ena-
bled and nothing is to be transmitted, the TDO
pin is at high level.
– RDI: Receive Data Input is the serial data input.
Oversampling techniques are used for data re-
covery by discriminating between valid incoming
data and noise.
Through this pins, serial data is transmitted and re-
ceived as frames comprising:
– An Idle Line prior to transmission or reception
– A start bit
– A data word (8 or 9 bits) least significant bit first
– A Stop bit indicating that the frame is complete.
This interface uses two types of baud rate generator:
– A conventional type for commonly-used baud
rates,
– An extended type with a prescaler offering a very
wide range of baud rates even with non-standard
oscillator frequencies.
14.5.4 LIN Protocol support
For LIN applications where resynchronization is
not required (application clock tolerance less than
or equal to 2%) the LIN protocol can be efficiently
implemented with this standard SCI.