Instruction Manual
3
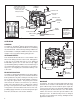
FIGURE 4 - BRAKE APPLICATION HOLDING
The pressure
under the piston
equals the
pressure above.
The piston lifts
slightly - the
exhaust remains
closed.
The driver
releases the
brakes. The
piston in the relay
valve moves
up, closing the
delivery, and
opening the
exhaust.
EXHAUST (OR RELEASE)
See Figure 5. When the driver releases the brake pedal, air
pressure above the relay piston is exhausted at the brake
valve exhaust. At the same time, air pressure beneath the
piston lifts the relay piston and the exhaust seat moves
away from the exhaust valve, opening the exhaust passage
at the base of the relay valve. With the exhaust passage
open, the air pressure from the brake chambers passes
to the Antilock Modulator Valve exhaust port, releasing the
brakes, and air pressure between the relay valve and the
modulator is released at the relay valve exhaust port.
TRACTION CONTROL
The ABS Controller monitors the driver’s accelerator
application, as well as the vehicle’s motion using wheel
speed sensors. When the vehicle is stopped, or moving
at any speed up to 25 mph and the Controller detects
wheel spin, for example where one wheel is slipping on
an icy patch, the ABS Controller will intervene to assist the
vehicle’s traction.
The ABS Controller obtains braking power for the traction
intervention by energizing the Control Solenoid in the
ATR-6
™
valve. This causes the traction piston to move to
its secondary position, allowing the supply air to operate the
relay piston and supply air pressure to each of its Antilock
Modulator Valves as shown in Figure 6.
The Controller then operates (opens and closes) the
solenoid valves in the individual Antilock Modulator Valve
for each spinning (slipping) wheel to slow that wheel. As the
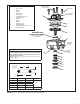
FIGURE 5 - BRAKE RELEASE
FIGURE 6 - TRACTION APPLICATION
The small piston moves to its energized
position. The arrow indicates the direction
it moves. The antilock traction Controller
energizes the solenoid, applying full reservoir
pressure to the antilock modulators.
The Controller
selects the
antilock
modulator to
deliver air to the
brake chamber
spinning wheel slows down, it forces the vehicle differential
to drive the other stationary, or slowly-turning wheel on that
axle, aiding the vehicle in gaining traction. Note: in some
vehicle arrangements a single modulator valve may control
air delivery to more than one brake chamber.