User's Manual
61-89A-50-A18-G1-UserMan page 9 of 20
TX RX Systems Inc. Manual 7-9352 (version 4) 01/27/04 Page 9
antenna or signal source and the output distri-
bution system does not exceed the signal
boosters gain by at least 15 dB. This condition
will reduce the effectiveness of the system and
may possibly damage the power amplifier
stages.
2) The major cause of damage to signal boosters
is the application of input RF power levels in
excess of the maximum safe input. This can
happen inadvertently when connecting a signal
generator with full power out to one of the inputs
or by a very strong signal that is far stronger
than expected. Following the pre-RF connection
checks listed next will help to avoid these two
problems.
PRE-RF CONNECTION TESTS
Certain characteristics of the signal distribution
system should be measured before connecting it to
the signal booster. This step is necessary to insure
that no conditions exist that could possibly damage
the signal booster and should not be skipped for
even the most thoroughly designed system. Two
characteristics need to be measured; antenna iso-
lation and input signal levels.
Test Equipment
The following equipment is required in order to per-
form the pre-installation measurements.
1) Signal generator for the frequencies of interest
capable of a 0 dBm output level. Modulation is
not necessary.
2) Spectrum analyzer that covers the frequencies
of interest and is capable of observing signal
levels down to -100 dBm.
3) Double shielded coaxial test cables made from
RG142 or RG55 coaxial cable.
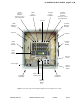
Antenna Isolation
Antenna isolation is the signal path isolation
between the two sections of the signal distribution
system that are to be connected to the signal
boosters antenna ports. Lack of isolation between
the input and output antennas can cause the
amplifiers in the system to oscillate. This can hap-
INTERNAL
SIGNAL DISTRIBUTION
SYSTEM
SPECTRUM
ANALYZER
EXTERNAL
ANTENNA
SIGNAL
GENERATOR
ZERO LOSS
REFERENCE
ISOLATION (dB)
Figure 2
: Typical test equipment setup for measuring antenna isolation.