Install Instructions
83
107750-01 - 9/17
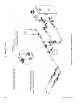
Figure 9.10: Isolation of the Boiler from Oxygenated Water with a Plate Heat Exchanger
IX. System Piping (continued)
D. Piping for Special Situations
1. Systems containing oxygen - Many hydronic systems contain enough dissolved oxygen to cause severe
corrosion damage to a this boiler. Some examples include:
• Radiant systems that employ tubing without an oxygen barrier.
• Systems with routine additions of fresh water.
• Systems which are open to the atmosphere.
If the boiler is to be used in such a system, it must be separated from the oxygenated water being heated with
a heat exchanger as shown in Figure 9.10. Consult the heat exchanger manufacturer for proper heat
exchanger sizing as well as ow and temperature requirements. All components on the oxygenated side of the
heat exchanger, such as the pump and expansion tank, must be designed for use in oxygenated water.
2. Piping with a Chiller - If the boiler is used in conjunction with a chiller, pipe the boiler and chiller in parallel.
Use isolation valves to prevent chilled water from entering the boiler.
3. Air Handlers - Where the boiler is connected to air handlers through which refrigerated air passes, use ow
control valves in the boiler piping or other automatic means to prevent gravity circulation during the cooling
cycle.