How to Guide
97
Pipe Size
In Inches
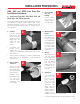
For systems where dismantling is required, flanging is a
convenient joining method. It is also an easy way to join plastic
and metallic systems.
Flange
Tightening
Sequence
Installation
1. Join the flange to
the pipe using the
procedures shown in the
solvent cementing or
threading sections. Due
to the tensile stresses
placed on the solvent
cement joint for flange
connections, double the recommended curing time before
joint assembly and pressure testing.
2. Use a full faced elastomeric gasket which is resistant
to the chemicals being conveyed in the piping system. A
gasket
1
⁄8
”
thick with a Durometer, scale “A”, hardness
of 55 -80 is normally satisfactory.
3. Align the flanges and gasket by inserting all of the bolts
through the mating flange bolt holes. Be sure to use
properly sized flat washers under all bolt heads and nuts.
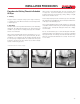
4. Sequentially tighten the bolts using a torque wrench,
corresponding to the patterns shown below in increments
of 10 ft-lbs at a time up to the recommended torque. New
bolts and nuts should be used for proper torque.
5. Tighten flanges only to maximum recommended torque
limits; do not tighten bolts in such a manner as to cause
the flange ring to bend or be under stress. Connect to full
face flanges or valves that conform to ANSI B16.5 150
pound dimensions and that provide full support under the
entire flange face.
Recommended Torque
No. Bolt
Holes
Bolt
Diameter
Recommended
Torque ft-lbs
Note: Flanges meet the bolt-pattern requirements of ANSI / ASME B 16.5
1
⁄2 4
1
⁄2 10 - 15
3
⁄4 4
1
⁄2 10 - 15
1 4
1
⁄2 10 - 15
1
1
⁄4 4
1
⁄2 10 - 15
1
1
⁄2 4
1
⁄2 10 - 15
2 4
5
⁄8 20 - 30
2
1
⁄2 4
5
⁄8 20 - 30
3 4
5
⁄8 20 - 30
4 8
5
⁄8 20 - 30
6 8
3
⁄4 33 - 50
8 8
3
⁄4 33 - 50
10 12
7
⁄8 53 - 65
12 12
7
⁄8 53 - 75
INSTALLATION PROCEDURES
6. Use a torque wrench to
tighten the bolts to the
torque values shown
below.
7. Use of thread lubricant
will ensure proper
torque. Confirm that
the thread lubricant is
chemically compatible
with pipe and fittings.
Flanges
• Exceeding recommended flange bolt torque may result in
component damage, system failure and property damage.
• Use the proper bolt tightening sequence as marked on the
flange.
• Make sure the system is in proper alignment.
• Flanges may not be used to draw piping assemblies
together.
• Flat washers must be used under every nut and bolt head.
• Connect to full face flanges or valves that conform to ANSI
B16.5 150 pound dimensions and that provide full support
under the entire flange face.
• Exceeding recommended pressure rating and/or
temperature ratings may result in component damage,
system failure and property damage.
• Ensure that thread lubricant is chemically compatible with
pipe and fittings.
• Piping systems differ in chemical resistance. Pipe or fittings
may be damaged by contact with products containing
incompatible chemicals resulting in system failure and/or
property damage.
• Corrosion resistant bolts, nuts, and flat washers are
recommended in chemical applications.
Testing with or use of compressed air or gas in PVC / ABS
/ CPVC pipe or fittings can result in explosive failures and
cause severe injury or death.
• NEVER test with or transport/store
compressed air or gas in PVC / ABS / CPVC
pipe or fittings.
• NEVER test PVC / ABS / CPVC pipe or
fittings with compressed air or gas, or air
over water boosters.
• ONLY use PVC / ABS / CPVC pipe or
fittings for water or approved chemicals.
• Refer to warnings on PPFA’s website and
ASTM D 1785.
1
1
1
2
2
2
6
10
4
44
8
12
5
9
3 3
8
7
6
5
3
7
11
8. When installing flanges in a buried application where
settling could occur, the flange must be supported to
maintain proper alignment in service.
For information on the pressure ratings of PVC and CPVC flanges please refer to the pressure rating of fittings, flanges, and
union sections in the design and engineering section of this manual.