C H A P T E R 1 Product Overview This chapter provides an overview of the Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 series routers. It contains physical descriptions of the router hardware and major components, and functional descriptions of the hardware-related features. Introduction The routers described in this guide are part of the Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 series routers and include: • The original Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 series routers. • The Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 enhanced series routers.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Product Description These two router models are differentiated by the switching capacity of the switch fabric installed in the router: • Cisco 12006 Router—2.5-Gbps switch fabric • Cisco 12406 Router—10-Gbps switch fabric Other than their various capacities, these routers are almost identical. Differences between each router are described unless otherwise noted, all information in this publication applies to all routers.
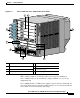
Chapter 1 Product Overview Product Description Figure 1-1 Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 router (Front View) 1 2 8 3 T EC EJ -1 OT SL -0 OT SL T SE RE X AU E LL CO RX OL NS -45 RJ CO K LIN TX I MI GIGABIT ROUTE PROCESSO R CISCO 120 00 GIGABIT SWIT SERIES CH ROU TER 101344 7 6 4 5 1 Line card slots (five) 5 Alarm card slots (two) 2 RP slot 6 Power module bays (two) 3 Blower module 7 CSC slots (two) 4 SFC slots (three) 8 Cable-management bracket With a chassis height
Chapter 1 Product Overview Product Description Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers have the following key features: • Route Processor (RP)—Slot 5 (bottom slot) is the recommended slot for the first RP. When the router is equipped with a redundant RP, it can be installed in any of the five regular line card slots. • Line Cards—Up to five OC-192 line cards, four if redundant RPs are installed.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Product Description • All power modules and other field replaceable units (FRUs), except for the air blower module and the power distribution unit (PDU), can be removed from the front of the chassis. • All source power connections are located at the rear of the chassis on the PDU. (See Figure 1-2.) • Enhanced models have a new stylish front door that hides router cabling. The door can be installed to open from the right side or left side to give you total flexibility.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Product Description Figure 1-2 Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 router (Rear View) 1 3 4 101114 HIGH SPEE D BLOWER 2 5 1 Blower module 4 Air exhaust vents 2 Blower module LEDs 5 PDU (behind Blower module; AC PDU shown) 3 Blower module handle – – • Fiber Cable Management—Fiber cable management with support for high-density fiber Fast Ethernet (FE) ports. • Current 1.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Physical and Functional Description Physical and Functional Description The main physical components of Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers and their functions are described in the following sections: • Chassis, page 1-7 • Multigigabit Crossbar Switch Fabric, page 1-10 • Maintenance Bus, page 1-13 • Route Processors, page 1-15 • Line Cards, page 1-33 • Alarm Cards, page 1-35 • Power Subsystems, page 1-37 • Blower Module, page 1-47 • Air Filters, page 1-49 • Ca
Chapter 1 Product Overview Chassis Switch Fabric Card Slots The switch fabric circuitry resides in five fabric card slots: two for CSCs and three for SFCs. (See Figure 1-1.) For more information about the role of the switch fabric circuitry, see the “Multigigabit Crossbar Switch Fabric” section on page 1-10. Alarm Card Slots Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers are equipped with two alarm cards. These cards are positioned beside one another and occupy two card slots directly under the CSC slots.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Chassis Power Because a Cisco 12006 or Cisco 12406 Router can be configured with either an AC-input power system or a DC-input power system, the power module bays will accept either AC-input power supply modules or DC-input PEMs. For more information about the power subsystems, see the “Power Subsystems” section on page 1-37. Caution To ensure that the chassis configuration complies with the required power budgets, use the on-line power calculator.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Multigigabit Crossbar Switch Fabric Multigigabit Crossbar Switch Fabric Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 router switch fabric circuity provides synchronized gigabit-speed interconnections for the line cards and the RP. The switch fabric circuitry resides in five fabric card slots: two for CSCs; three for SFCs. (See Figure 1-3.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Multigigabit Crossbar Switch Fabric • System clock—The system clock synchronizes data transfers between line cards or between the RP and a line card, through the switch fabric. In systems with redundant CSCs, the two system clocks are synchronized so that if one system clock fails, the other clock takes over. The system clock signal is sent to all line cards, the RP, and switch fabric cards.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Multigigabit Crossbar Switch Fabric Switch Fabric Switching Capacity and Router Type The Cisco 12006 Router is based on a 2.5-Gbps switch fabric, where each CSC or SFC provides a 2.5-Gbps full-duplex connection to each line card in the system. The 2.5-Gbps switch fabric consists of the 12006 Advanced Clock and Scheduler Card (product number 12006-CSC=) and the 12006 Advanced Switch Fabric Card (product number 12006-SFC=). The 2.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Maintenance Bus Maintenance Bus The Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 router maintenance bus and MBus modules manage the maintenance functions of the system. The MBus is integrated into the backplane and consists of two separate buses, providing MBus redundancy.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Maintenance Bus Code Download A portion of the line card operating software can be downloaded from the RP to the line card over the MBus. Because the MBus is relatively slow compared to the switch fabric, only enough code is downloaded to the line card for it to access the switch fabric and complete the download process. Diagnostics The diagnostic software image is downloaded from the RP to the line card during the test sequence.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Route Processors Each Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 router has one main system (or route) processor. The route processor (RP) processes the network routing protocols and distributes updates to the Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) tables on the line cards. The RP also performs general maintenance functions, such as diagnostics, console support, and line card monitoring.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Route Processor Types Two types of RPs are available for Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers, the Gigabit Route Processor (GRP), and the Performance Route Processor (PRP). Each of these route processor types is reviewed in the following sections: • Gigabit Route Processor, page 1-16 • Performance Route Processor, page 1-25 When not explicitly specified, this document uses the term route processor (RP) to indicate either the GRP or the PRP.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Note GRP route memory configurations of 512 MB are compatible with only Product Number GRP-B=. Cisco IOS Release 12.0(19)S or 12.0(19)ST or later, and ROMMON Release 11.2 (181) or later are also required. • SRAM—512 kilobytes (KB) of static random-access memory (SRAM) for secondary CPU cache memory functions. SRAM is not user configurable or field upgradeable. • NVRAM—512 KB of nonvolatile RAM (NVRAM). NVRAM is not user configurable or field upgradeable.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Figure 1-5 GRP Layout Backplane connector U42 Bank 2 DRAM DIMMs Bank 1 U39 Flash SIMM EJ EC T -1 OT SL -0 OT SL RE SE CO T X AU LIN PCMCIA slots slot 0: bottom slot 1: top K TX LL RJ RX M -4 H10547 U17 5 II Auxiliary port Console port GIGABIT ROUTE PROCESSOR Alphanumeric LED displays Ethernet interface (RJ-45 or MII) Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 Router Installation and Configuration Guide 1-18 OL-11497-03
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors GRP Memory Components Table 1-1 lists the memory components on the GRP. Figure 1-5 shows the location of the DRAM and Flash SIMM on the GRP.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Table 1-2 Total DRAM GRP DRAM Configurations Product Numbers DRAM Sockets Number of DIMMs MEM-GRP/LC-64(=) U39 (bank 1) and U42 (bank 2) 2 64-MB DIMMs 128 MB MEM-GRP/LC-128(=) U39 (bank 1) 1 128-MB DIMM 256 MB MEM-GRP/LC-256(=) U39 (bank 1) and U42 (bank 2) 2 128-MB DIMMs 128 MB 1 1. 128 MB is the standard (default) DRAM configuration for the GRP. Caution To prevent memory problems, DRAM DIMMs must be 3.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Flash memory also functions as a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server to allow other servers to boot remotely from stored images or to copy them into their own Flash memory. The onboard Flash memory (called bootflash) contains the Cisco IOS boot image, and the Flash memory card contains the Cisco IOS software image. To order a spare Flash memory card, use Cisco product number MEM-GRP-FL20=, which is a 20-MB Type II PCMCIA Flash memory card.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Figure 1-7 GRP Alphanumeric LED Displays (Partial Faceplate) Right alphanumeric LED display (four digits) 57079 Left alphanumeric LED display (four digits) The alphanumeric LED displays router status messages: • Router status messages that are displayed during the boot process • Router status messages that are displayed after the boot process is complete During the boot process, the alphanumeric LED message displays are controlled directly by the MBus m
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors For example, when the boot field of the software configuration register is set to 0x0 and you press the NMI switch, the GRP remains at the ROM monitor prompt (rommon>) and waits for a user command to boot the system manually. If the boot field is set to 0x1, the system automatically boots the first Cisco IOS image found in the onboard Flash memory SIMM on the GRP.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Note EIA/TIA-232 is also referred to as RS-232. The auxiliary port is an EIA/TIA-232 plug (male) that provides a data terminal equipment (DTE) interface. The auxiliary port supports flow control and is often used to connect a modem, a channel service unit (CSU), or other optional equipment for Telnet management. Note In order to maintain Class B EMI compliance, shielded cables must be used on the console and auxiliary ports of the GRP= and GRP-B=.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Performance Route Processor This section provides information about the PRP. The PRP is supported in both the Cisco 12406 Router and the Cisco 12006 Router. Figure 1-8 shows the front panel view of the PRP. The PRP is shipped with 20 MB of Flash memory as the default configuration.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors The Cisco IOS software images are stored in Flash memory. Two types of Flash memory ship with the PRP: 1. Onboard Flash memory—Ships as a single in-line memory module (SIMM). This Flash memory contains the Cisco IOS boot image (bootflash) and is not field replaceable. 2. Flash disk—The PRP ships with a Flash disk that can be installed in either Flash disk slot. (See Figure 1-9.) The Flash disk contains the Cisco IOS software image.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Figure 1-9 PRP (Horizontal Orientation) 1 3 2 ETH 0 -1 OT SL -0 OT SL AUX TX K LIN T 6 SE 5 PRIMARY CONSOLE RX EN RE PRIMARY 4 ETH 1 RX TX EN K LIN 7 8 1 Backplane connector 6 Ethernet ports 2 Flash SIMM (Socket number P3) 7 Auxiliary port 3 SDRAM DIMMs Bank 1 - Socket number U15 Bank 2 - Socket number U18 8 Console port 4 Ejector lever 9 Handle 5 Flash disk slots (covered) 10 Display LEDs PERFORMANCE ROUTE PROCESSOR 1 (PRP
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors PRP Memory Components PRP memory options and functions are listed in Table 1-4.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors SDRAM SDRAM stores routing tables, protocols, and network accounting applications, and runs the Cisco IOS software. The default PRP configuration includes 512 MB of error checking and correction (ECC) SDRAM. DIMM upgrades of 512 MB and 1 GB are available. You cannot mix memory sizes. If two DIMMS are installed, they must be the same memory size. Caution Cisco Systems strongly recommends that you use only Cisco-approved memory.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors the Flash disk contains the Cisco IOS software image. A 64-MB ATA Flash disk ships by default with the PRP. Table 1-5 lists the supported Flash disk sizes and their Cisco product numbers. Table 1-5 Supported Flash Disk Sizes and Product Numbers Flash Disk Size1 64 MB2 Product Number MEM-12KRP-FD64= 128 MB MEM-12KRP-FD128= 1 GB MEM-12KRP-FD1G= 1.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors At the end of the boot process, the LEDs are controlled by the Cisco IOS software (via the MBus), and the content displayed is designated by the Cisco IOS software. The display LEDs indicate the following information: Note • Status of the PRP • System error messages • User-defined status and error messages A complete, descriptive list of all system and error messages is located in the Cisco IOS System Error Messages publications.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Route Processors Flash Disk Slots The PRP includes two Flash disk (PCMCIA) slots. Either slot can support an ATA Flash disk or a Type 1 or Type 2 linear Flash memory card. The PRP ships by default with one 64-MB ATA Flash disk. Note The PRP only supports +5 VDC Flash disk devices. It does not support +3.3 VDC PCMCIA devices. The PRP supports different combinations of Flash devices.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Line Cards Line Cards Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers come pre-installed with the number and type of line cards that you ordered. Line cards and RPs can be installed in two basic combinations to support RP redundancy and a variety of physical network media: • Nonredundant RP—One RP and up to five Cisco 12000 Series Router line cards. • Redundant RPs—Two RPs and up to four Cisco 12000 Series Router line cards.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Line Cards Figure 1-10 Sample Line Cards Multimode Single Mode Ejector lever 0 ER VE I KT TI RR P AC CA RX ER VE I KT TI RR P AC CA RX Status LEDs 1 1 Port 1 ER VE I KT TI RR P AC CA RX ER VE I KT TI RR P AC CA RX 2 2 Port 2 ER VE I KT TI RR P AC CA RX ER VE I KT TI RR P AC CA RX 3 3 Port 3 ER VE I KT TI RR P AC CA RX ER VE I KT TI RR P AC CA RX Alphanumeric LED display Q OC-3/STM-1 MM POS Q OC-3/STM-1 SM IR POS 160-pin backplane signal connector H10781
Chapter 1 Product Overview Line Cards Alarm Cards Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers have two alarm card slots. Each alarm card performs the following function or indicates the following condition: • Alarm output • CSC status • SFC status • Alarm card status • Power source and power entry module status • Alarm relay contacts The entire alarm function has been implemented on redundant alarm cards with OIR maintenance (hot-swappable) functionality.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Line Cards Alarm Output Function The alarm output function consists of a group of relays, LEDs, and their associated drivers connected to an output port on the MBus module. The alarm output function is controlled by the software on the RP. When a signal is received from the RP, the MBus module on the alarm card activates specific relays to signal an alarm condition. There are three alarm condition severity levels: critical, major, and minor.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Power Subsystems Power Source Monitoring The alarm card monitors the power modules and signals when there is a condition outside the normal range of operation.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Power Subsystems Note Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers can be either AC powered or DC powered; the router cannot accept two different types of power modules at the same time. For detailed handling and replacement instructions for the Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 router power supplies or PEMs, see Chapter 6, “Maintaining the Router,” or refer to the appropriate configuration note for the power supply or PEM that is shipped from the factory as an FRU.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Power Subsystems Figure 1-12 AC Power Distribution Unit 1 4 3 5 57650 6 2 1 Captive screw 4 AC power distribution unit 2 AC power cord receptacle A 5 Guide pin 3 AC power cord receptacle B 6 Blower module connector Depending on whether the router is configured for nonredundant or redundant power operation, the router ships with either one or two 14-foot (4.3-m) AC power cords to connect the PDU to the facility AC power source.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Power Subsystems AC-Input Power Supply The AC-input power supply is a removable power module that installs in one of the bottom two bays on the front of the chassis (see Figure 1-1). These power modules support the OIR feature and are hot-swappable.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Power Subsystems An AC-input power supply (shown in Figure 1-13) has the following features: • A power factor corrector (PFC) allows the power supply to accept AC power source voltage from an AC power source operating from 100 to 240 VAC 20-amp service in North America, and a range of from 185 to 264 VAC 16-amp service in an international environment. • Each AC-input power supply weighs 14 pounds (6.4 kg), and can deliver up to 1400 Watts (W) at –54.5 VDC.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Power Subsystems • Two LEDs on the faceplate to provide status information. Table 1-6 summarizes the function of these indicators. Table 1-6 AC-Input Power Supply LED indicators LED Label Function State Description AC Input power On AC power source is present and is within specified limits. Off Power source is not within specified limits. On Power supply is operating normally in a power-on condition.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Power Subsystems Figure 1-14 DC Power Distribution Unit 1 4 PO WE RB + GN D 3 5 PO WE RA 6 + GN 2 1 Captive screw 4 DC power distribution unit 2 DC power connector block A 5 Guide pin 3 DC power connector block B 6 Blower module connector 57992 D DC-input power is connected through the DC PDU on the chassis rear panel. The DC PDU is equipped with two DC power connector blocks. Each DC power connector block is equipped with three terminal ports.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Power Subsystems power should be connected to the terminal block. A negative lead is connected to the top port, a positive lead to the middle port, and a ground lead to the bottom port. (See Figure 1-15.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Power Subsystems Figure 1-16 DC-Input Power Entry Module 62203 OUTPUT INPUT MISWIR OK E OK OUTPUT INPUT MISW OK IRE OK 5 4 4 2 3 1 1 DC-input PEM 4 Captive screws on release levers 2 Handle 5 Air inlet for cooling fan 3 Circuit breaker ON/OFF switch – – A DC-input PEM (shown in Figure 1-16) has the following features: • A circuit breaker switch on the faceplate turns the PEM on and off. • A handle is provided for ease in removing and replacing the PEM.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Power Subsystems • Three LEDs on the faceplate to provide status information. Table 1-7 summarizes the function of these indicators. Table 1-7 DC-input PEM LED Indicators LED Label Color Function OUTPUT OK Green PEM is operating normally in a powered-on condition. INPUT OK Green DC power is present at the PEM input and within the specified limits. MISWIRE Amber Indicates input is wired backward at the PDU input. • Each PEM weighs 10.5 pounds (4.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Blower Module Power Distribution The router chassis backplane distributes -48 VDC power throughout the router and to all cards in the card cages. All cards have multiple DC-DC converters that convert the -48 VDC into +2.5 VDC, +3.3 VDC, +5 VDC, and other voltages as required by the line card. The DC-DC converters are turned on by the MBus modules under the control of the RP and MBus software.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Blower Module If the air temperature inside the RP and line card cage rises, the system environmental monitor shuts down all internal power to prevent equipment damage from excessive heat. If the system detects that one of three fans within a blower module has failed, it displays a warning message on the console screen. If multiple fans fail, the system shuts down to prevent equipment damage.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Blower Module • OK—Left LED; Green. When on, this LED indicates that the blower module is operating normally. This LED should come on as soon as the blower module is installed and receives power from the backplane connector. • FAIL—Right LED; Red. The red LED should remain off during normal operation. If the red LED is on, the system has detected a fan failure or other fault in the blower module. Replace the existing blower module with a spare.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Cable-Management System The air filters are located on the right of the front side of the chassis. The air filters are housed behind a door that is spring-loaded in the closed position. Caution Air filters should be clean when the router is operating. Inspect and clean the air filters once a month, more often in dusty environments. Do not run the router without the air filters installed.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Cable-Management System On line cards with multiple ports, the line card cable-management bracket keeps the network interface cables organized when your remove and replace the line card. You can unplug the network interface cables from their connectors on the line cards and leave the cables bundled in the line card cable-management bracket while you remove the bracket from the line card.
Chapter 1 Product Overview Field-Replaceable Units Field-Replaceable Units The field-replaceable units (FRUs) for Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers include the following units: • Route processor • Line cards • CSCs • SFCs • Alarm cards • PDU: – For AC powered systems, AC PDU – For DC-powered systems, DC PDU • Power modules: – For AC-powered systems, AC-input power supplies – For DC-powered systems, DC-input PEMs • AC power cords (for AC powered systems) • Blower module • Air filters