User manual
33
same with the network you are connecting to.
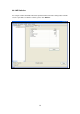
Network
Authentication
This setting has to be consistent with the wireless networks that
the adapter intends to connect to.
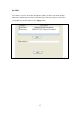
Open System – No authentication is needed to connect to the
wireless network.
Shared Key – Only wireless stations using a shared key (WEP
Key) are allowed to connect to each other.
WPA-PSK – Is a special protected access designed for home and
small business users who do not have access to network
authentication servers. In this mode, known as Pre-Shared Key,
the user manually enters the starting password in their access
point or gateway, as well as in each wireless stations in the
network. WPA-PSK takes over automatically from that point,
preventing unauthorized users that don‟t have the matching
password from joining the network, while encrypting the data
traveling between authorized devices.
WPA2-PSK – WPA2-PSK is also for home and small businesses.
The difference between WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK is that
WPA2-PSK provides data encryption via AES. In contrast,
WPA-PSK uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP).
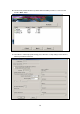
Data Encryption
Disabled – Disable the WEP Encryption.
WEP – Enable WEP Encryption. When WEP is selected, you have
to continue setting the WEP keys.
TKIP – TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) changes the
temporal key every 10,000 packets (a packet is a kind of message
transmitted over a network.) This insures much greater security
than the standard WEP security.
AES – AES has been developed to ensure the highest degree of
security and authenticity for digital information and it is the most
advanced solution defined by IEEE 802.11i for security in wireless
networks.
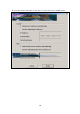
Note: All devices in the network should use the same encryption
method to ensure proper communication.