User manual
89
7.2 Security
Security options include authentication and encryption services based on the wired
equivalent privacy (WEP) algorithm. WEP is a set of security services used to
protect 802.11 networks from unauthorized access, such as eavesdropping; in this
case, the capture of wireless network traffic. When data encryption is enabled,
secret shared encryption keys are generated and used by the source station and the
destination station to alter frame bits, thus avoiding disclosure to eavesdroppers.
802.11 supports two subtypes of network authentication services: open system and
shared key. Under open system authentication, any wireless station can request
authentication. The system that needs to authenticate with another wireless
station sends an authentication management frame that contains the identity of the
sending station. The receiving station then sends back a frame that indicates
whether it recognizes the identity of the sending station.
Under shared key authentication, each wireless station is assumed to have received
a secret shared key over a secure channel that is independent from 802.11 wireless
network communications channel.
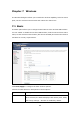
The following screen appears when Security is selected. The Security page allows
you to configure security features of the wireless LAN interface. You can set the
network authentication method, selecting data encryption, specify whether a
network key is required to authenticate to this wireless network and specify the
encryption strength.
Click Apply to configure the wireless security options.