Installation manual
ISDN (Integrated System Digital Network)
The digital ISDN is a communication network where the line from the exchange
equipment and the service supplied to the subscriber is ‘digital’, i.e. not ‘ana-
logue’.
An ISDN line is a digital telephone line that conforms to the international ISDN
standard. It can carry several calls simultaneously. A ‘basic rate’ ISDN tel-
ephone line can carry the equivalent of two simultaneous calls. In UK, a ‘basic
rate’ ISDN line is called ISDN2 or ISDN2e. A ‘primary rate’ ISDN line can carry
the equivalent of up to thirty simultaneous calls. In UK, a ‘primary rate’ ISDN
line is called ISDN30.
An ISDN line is always terminated at the users premises by an NTP (Network
Termination Point) which is provided by the telecoms Service Provider. The NTP
is a socket or connection where the users equipment can be connected.
The service supplied to the user from the NTP may vary. The digital connection
on the NTP is called the S-Bus. The S-Bus allows many different types of
digital communication equipment to be connected, e.g. an ISDN interface card
in a PC.
In many cases, the ISDN NTP operates using power supplied from the ex-
change equipment via the ISDN telephone line, however some types of NTP
may require a connection to the mains supply at the users premises. Some
ISDN NTPs include a converter to provide analogue sockets (e.g. Home High-
way); See below.
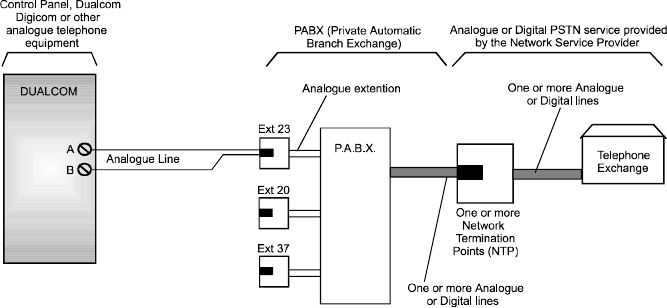
PABX with Analogue extension
Fig 13
25










