User manual
CRADLEPOINT MBR1400 | USER MANUAL – Firmware version 4.2
© 2013 CRADLEPOINT, INC. PLEASE VISIT HTTP://KNOWLEDGEBASE.CRADLEPOINT.COM/ FOR MORE HELP AND RESOURCES PAGE 88
Redistribute Routes: Redistribute routes of the specified protocol or
kind into BGP, with the metric type and metric set (if specified), filtering
the routes using the given route map (if specified). Redistributed routes
may also be filtered with distribute lists.
• Type: The type is the source of the route. Select from: Main,
Connected, Static, RIP, OSPF.
• Metric: Numerical priority of the route.
• Route Map: Route maps provide a means to filter and/or apply
actions to routes, allowing policies to be applied to routes.
6.7.3 RIP Routing Protocol
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a widely deployed interior gateway protocol. RIP is a distance-vector protocol based
on the Bellman-Ford algorithms. As a distance-vector protocol, RIP sends updates from one router to its neighbors
periodically, allowing the convergence to a known topology. In each update, the distance to any given network will be
broadcast to its neighboring router. The router supports RIP version 2 as described in RFC2453 and RIP version 1 as
described in RFC1058.
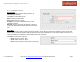
RIP Editor
• Name: Unique name of the policy.
• Metric: RIP metric is a value for distance for the
network. Usually RIP increments the metric when
the network information is received. The metric for
redistributed routes is set to 1.
• Protocol Version: RIP can be configured to send
either Version 1 or Version 2 packets. The default
is to send RIPv2 while accepting both RIPv1 and
RIPv2 (and replying with packets of the appropriate