Specifications
Table Of Contents
- Coverpage
- Safety Instructions
- Revision History
- Contents
- Introduction
- 1 Outline
- 2 Explanation of Functions
- 3 Q-PLC Multi-CPU
- 4 Q Motion CPU
- 5 SFC Program
- 6 SV22 Servo Programs
- 6.1 Servo program
- 6.1.1 Servo program configuration
- 6.1.2 List of servo commands
- 6.1.3 Linear control
- 6.1.4 Circular interpolation control using auxiliary point designation
- 6.1.5 Circular interpolation control using radius designation
- 6.1.6 Circular interpolation control using center point designation
- 6.1.7 Fixed-dimension feed control
- 6.1.8 Speed control
- 6.1.9 Speed/position changeover control
- 6.1.10 Speed changeover control
- 6.1.11 Constant-speed control
- 6.1.12 Repeated control (for speed changeover control and uniform speed control)
- 6.1.13 Simultaneous start
- 6.1.14 Zero point return
- 6.1.15 Position follow-up control
- 6.1.16 High-speed oscillation control
- 6.1.17 Helical interpolation control with auxiliary point designated
- 6.1.18 Helical interpolation control with radius designated
- 6.1.19 Helical interpolation control with center point designated
- 6.1.20 Current value change
- 6.1 Servo program
- 7 Operation Control Program
- 8 Windows Personal Computer Operations
- 9 Basic Practice Using the SV22 Real Mode
- 10 Applied Practice with SV22 Real Mode
- 10.1 Details of practice
- 10.2 Q172CPU practice machine system configuration
- 10.3 Practice SFC programs
- 10.4 Writing to the motion CPU
- 10.5 Program for operation
- 10.5.1 JOG operation
- 10.5.2 Main routine SFC program (real mode operation)
- 10.5.3 Execution of servo program (motion control step)
- 10.5.4 Stopping
- 10.5.5 Error reset
- 10.5.6 Current value change
- 10.5.7 Speed change (CHGV)
- 10.5.8 Reading actual current value
- 10.5.9 Continuous positioning
- 10.5.10 M code function
- 10.5.11 Indirect setting of servo program address
- 10.6 Operating the practice machine
- 11 Practicing with the SV22 Virtual Mode
- 11.1 Mechanism program
- 11.2 Details of practice
- 11.3 Starting up SW3RN-CAMP and creating the cam
- 11.4 SFC program for virtual mode
- 11.5 Editing the mechanism
- 11.6 Writing to the motion CPU
- 11.7 Reading of sequence program from Q-PLC CPU
- 11.8 SFC program for practice
- 11.9 Practice machine operations
- 11.10 Exercise (Roller setting)
- Appendix
A - 48
IN POSITION
Signal that relies on the positioning data's
servo parameters. The droop pulse amount in
the deviation counter (difference of position
feedback from position command value and
servomotor) is detected, and if the result
matches the setting value, this signal turns
ON.
This can be used to disregard fractional droop
pulses, and start the next positioning.
INSTALLATION FUNCTION
The OS (operating system) in the motion
controller can be rewritten with a peripheral
device. The OS includes SV13 for the transfer
assembly machine, SVC22 for the automatic
machine, SV43 for the machine tool peripheral
device and SCV41 for the dedicated robot.
Usage that matches each machine can be
realized by installing the OS.
INVERTER
This refers to a device to change a direct
current (DC) to an alternating current (AC).
The device actually changes the motor speed
by changing 50Hz or 60Hz of commercial
frequency to direct current once, then
changing it again to a 5 to 120Hz alternating
current and controlling the motor speed.
JERK
The acceleration rate is differentiated by time
to indicate the acceleration rate change rate.
JOG
This refers to moving the tool in small steps at
a time. Inching.
JOG operation can be carried out with test
operation of a peripheral device, and from the
sequence program by writing in the
parameters and JOG speed.
kPPS
This is the abbreviation for "kilopulses per
second". 80kPPS equals 80,000 pulses per
second.
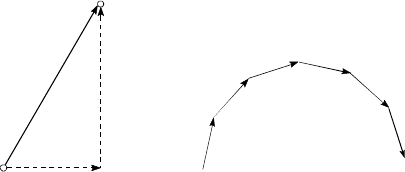
LINEAR INTERPOLATION
Automatic operation, in which the CPU makes
calculations so that the axis moves along a
straight line when positioning is carried out by
simultaneously operating both the longitudinal
feed and latitudinal feed motors.
The types include ABS-2, INC-2, ABS-4 and
INC-4.
An example of 2-axis linear interpolation is
shown on the right.
No.9
No.8
No.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Longitudinal
feed
Latitudinal feed
LINE MONITORING
Refers to monitoring the control status of the
PLC and controller during operation.
LOAD INERTIA RATIO
GD
L
2
/GD
M
2
Refer to "GD
2
".
LOW-INERTIA MOTOR
This is a motor used when frequent
acceleration/deceleration is repeated. Low-
inertia motors are longitudinally longer, to
decrease the rotor diameter and cover the
torque. This enables their inertia moment to be
reduced up to 1/3 that of standard motors. The
ideal load inertia ratio is 1 or less.
MACHINE NAME (System Name)
This is a sign of up to 8 characters that the
user can choose and assign to a file name.
Alphabetic characters (uppercase), numerals,
and minus (–) signs can be used. The first
character is an alphabetic character.
Refer to the term "FILE NAME".










