Specifications
Table Of Contents
- Coverpage
- Safety Instructions
- Revision History
- Contents
- Introduction
- 1 Outline
- 2 Explanation of Functions
- 3 Q-PLC Multi-CPU
- 4 Q Motion CPU
- 5 SFC Program
- 6 SV22 Servo Programs
- 6.1 Servo program
- 6.1.1 Servo program configuration
- 6.1.2 List of servo commands
- 6.1.3 Linear control
- 6.1.4 Circular interpolation control using auxiliary point designation
- 6.1.5 Circular interpolation control using radius designation
- 6.1.6 Circular interpolation control using center point designation
- 6.1.7 Fixed-dimension feed control
- 6.1.8 Speed control
- 6.1.9 Speed/position changeover control
- 6.1.10 Speed changeover control
- 6.1.11 Constant-speed control
- 6.1.12 Repeated control (for speed changeover control and uniform speed control)
- 6.1.13 Simultaneous start
- 6.1.14 Zero point return
- 6.1.15 Position follow-up control
- 6.1.16 High-speed oscillation control
- 6.1.17 Helical interpolation control with auxiliary point designated
- 6.1.18 Helical interpolation control with radius designated
- 6.1.19 Helical interpolation control with center point designated
- 6.1.20 Current value change
- 6.1 Servo program
- 7 Operation Control Program
- 8 Windows Personal Computer Operations
- 9 Basic Practice Using the SV22 Real Mode
- 10 Applied Practice with SV22 Real Mode
- 10.1 Details of practice
- 10.2 Q172CPU practice machine system configuration
- 10.3 Practice SFC programs
- 10.4 Writing to the motion CPU
- 10.5 Program for operation
- 10.5.1 JOG operation
- 10.5.2 Main routine SFC program (real mode operation)
- 10.5.3 Execution of servo program (motion control step)
- 10.5.4 Stopping
- 10.5.5 Error reset
- 10.5.6 Current value change
- 10.5.7 Speed change (CHGV)
- 10.5.8 Reading actual current value
- 10.5.9 Continuous positioning
- 10.5.10 M code function
- 10.5.11 Indirect setting of servo program address
- 10.6 Operating the practice machine
- 11 Practicing with the SV22 Virtual Mode
- 11.1 Mechanism program
- 11.2 Details of practice
- 11.3 Starting up SW3RN-CAMP and creating the cam
- 11.4 SFC program for virtual mode
- 11.5 Editing the mechanism
- 11.6 Writing to the motion CPU
- 11.7 Reading of sequence program from Q-PLC CPU
- 11.8 SFC program for practice
- 11.9 Practice machine operations
- 11.10 Exercise (Roller setting)
- Appendix

6 - 9
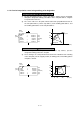
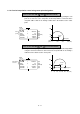
6.1.4 Circular interpolation control using auxiliary point designation
2-axis control with ABS (absolute method)
(1) Circular interpolation from the current stop address (address before positioning)
through the designated auxiliary point address to the end point address, using the
zero point as the reference.
(2) The center of the arc is the point of intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of
the start point address (current stop address) to the auxiliary point address, and
the auxiliary point address to the end point address.
200
100
0
0 100 200 300 (mm)
1,
2,
1,
2,
200000.0
200000.0
5000.00
50000.0
150000.0
150
50
REAL
<K 52>
ABS
AXIS
AXIS
SPEED
PAS-PT.
PAS-PT.
End
point
(µm)
(µm)
(mm/min)
(µm)
(µm)
Start point
Auxiliary
point
End point
2-axis control with INC (increment method)
(1) Circular interpolation takes place from the current stop address, past the
designated auxiliary point to the end point.
(2) An arc, having as its center point the intersection of the vertical bisector consisting
of the start point (current stopped position) to auxiliary point, and auxiliary point to
end point, is formed.
200
100
0
0 100 200 300 (mm)
1,
2,
1,
2,
200000.0
150000.0
5000.00
50000.0
100000.0
50
50
150
REAL
<K 53>
INC
AXIS
AXIS
SPEED
PAS-PT.
PAS-PT.
End
point
(µm)
(µm)
(mm/min)
(µm)
(µm)
Start point
Auxiliary
point
End point