User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- 1.1 Overview
- 1.2 General Parameters
- 1.3 Electrical and Thermal Characteristics
- 1.4 Pinout Diagram
- 1.5 Pinout Listing
- 1.6 Package Description
- 1.7 System Design Information
- 1.8 Ordering Information
- A.1 Package Environmental, Operation, Shipment, A....
- A.2 Card Assembly Recommendations
603 Hardware Specifications, REV 2 25
Preliminary—Subject to Change without Notice
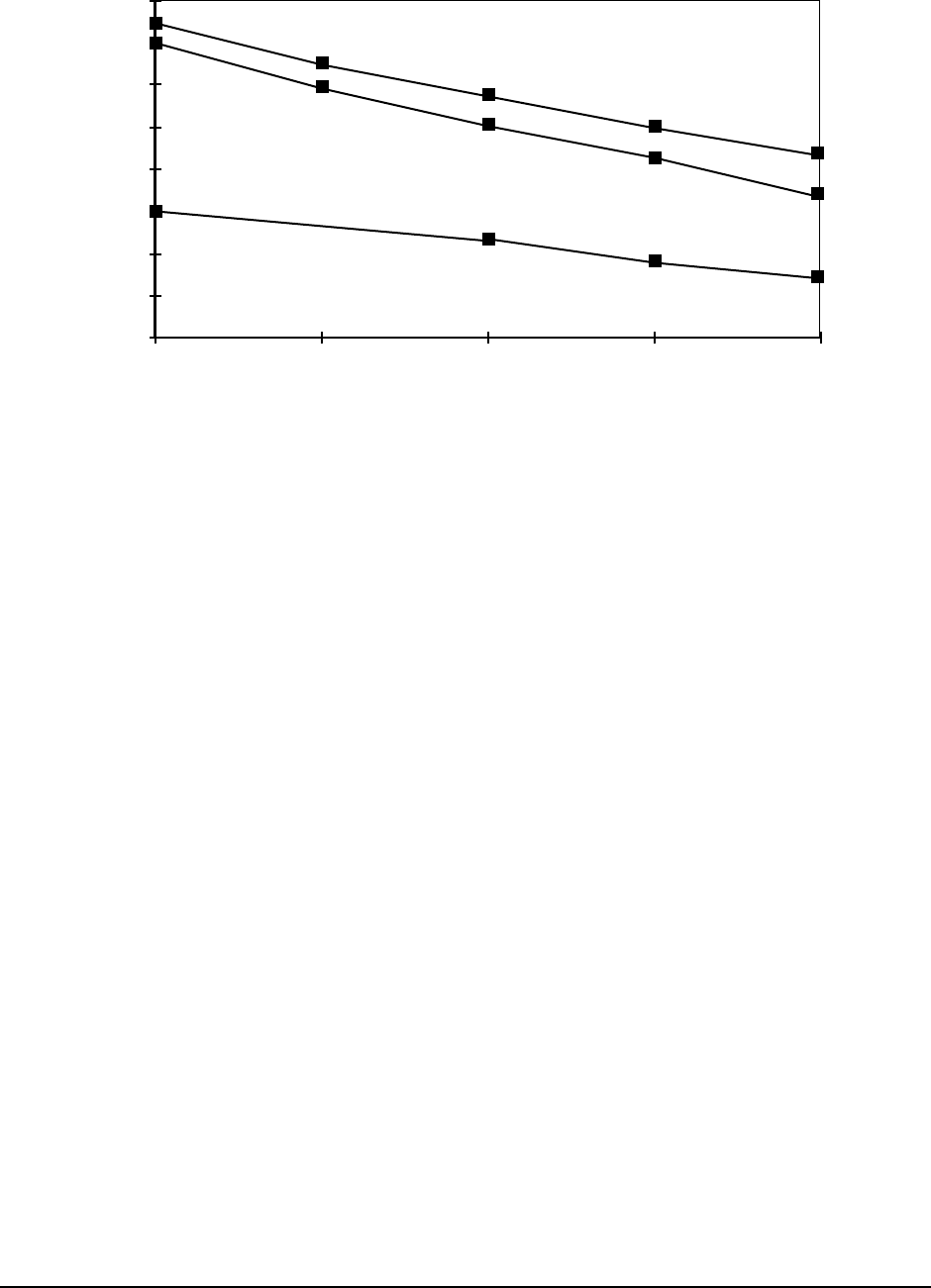
Figure 14 provides a thermal management example for the IBM C4-CQFP package.
Figure 14. IBM C4-CQFP Thermal Management Example
For a power dissipation of 2.5 Watts in an ambient temperature of 40 °C at 1 m/sec with the pinfin heat sink
measured above, the junction temperature of the device would be as follows:
T
j
= T
a
+ R
θja
* P
T
j
= 40 °C + (9.1 °C/Watt * 2.5 Watts) = 63 °C
which is well within the reliability limits of the device.
Notes: 1. Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance is based on modeling.
2. Junction-to-heat sink thermal resistance is based on measurements and model using thermal test
chip and thermal couple which is placed on the base of the heat sink.
3.
θ
ja
is not measured for 0.25 m/sec convection for the pinfin.
The vendors who supply heat sinks are Aavid Engineering, Thermalloy, and Wakefield Engineering. Any of
these vendors can supply heat sinks with sufficient thermal performance.
Forced Convection (m/sec)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
0 0.25 0.5 1 2
Exposed Die
Aluminum
Plate
Pinfin
Junction-to-Ambient
Thermal Resistance (°C/W)
IBM C4-CQFP