Release Notes
Optimize an SC Series array for an Oracle data warehouse
14 Optimizing Dell EMC SC Series Storage for Oracle OLAP Processing | 2009-M-BP-O
The following list shows an example of how to apply different storage profiles to different data types:
• Dell EMC and Oracle recommend using Oracle ASM to manage the data storage.
• The same storage profile must be applied to each SC Series volume that constitutes the ASM disk
groups.
• In most cases, the predefined Recommended profile offers the most effective way to manage data
across all storage tiers and RAID levels. The Recommended profile dictates that new data writes to
tier 1 R10, moves snapshot data to R5/R6 within the same tier, and moves aged or inaccessible data
to tier 3.
• Alternatively, certain data, such as summarized data and historical data, can be restricted to storage
tier(s) by assigning the tier specific storage profiles such as High Priority or Low Priority. Data can
still move between different RAID levels within the same tier to gain efficiency. This offers
administrators more precise control over the data placement when appropriate.
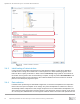
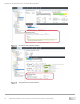
• Storage profiles can be set or changed in the Edit Volume dialog box in DSM at any time (see Figure
3). Therefore, administrators can experiment with the different storage profiles to find the best fit for
their needs. Data Progression moves data into appropriate tiers during the next Data Progression
cycle without impacting running applications.
Table 2 offers an example of selected storage profiles on the three data warehouse data types.
Data warehouse data types and storage profiles
ASM disk
groups
Data type
Storage
profiles
Storage
tiers/RAID
levels
Description
+DATA1DG
Historical
data
Recommended
All tiers/
all RAID
levels
• Consumes large amount of storage
• Predictable and consistent growth
• Data is mostly read-only
• New data is written to the fastest write
layer T1 R10
• Active data remains in T1
• Aged data moves to T3 R5 or R6 which
offers the same read performance as
R10 but takes less space
Low Priority
(Tier 3)
T3/
all RAID
levels
• New data writes to the fastest write
layer T3 R10
• Active data remains in T3 R10
• Aged data moves to T3 R5 or R6 which
offers as good read performance as
R10 with less space
+DATA2DG
Summarized/
calculated
data
Recommended
All tiers/
all RAID
levels
• New data writes to the fastest write
layer T1 R10
• Active data remains on T1
• Aged data moves to T3 R5 or T6 which
offers as good read performance as
R10 with less space