Administrator Guide
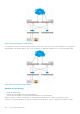
Figure 133. Packets without peer routing enabled
If you enable peer routing, a VLT node acts as a proxy gateway for its connected VLT peer as shown in the image below. Even though the
gateway address of the packet is different, Peer-1 routes the packet to its destination on behalf of Peer-2 to avoid sub-optimal routing.
Figure 134. Packets with peer routing enabled
Benefits of Peer Routing
•
• Avoids sub-optimal routing
• Reduces latency by avoiding another hop in the traffic path.
• You can reduce the number of VLTi port channel members based on your specific design.
With peer routing, you need not configure VRRP for the participating VLANs. As both VLT nodes act as a gateway for its peer,
irrespective of the gateway IP address, the traffic flows upstream without any latency. There is no limitation for the number of VLANS.
880
Virtual Link Trunking (VLT)