Concept Guide
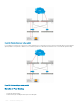
Figure 133. Packets without peer routing enabled
If you enable peer routing, a VLT node acts as a proxy gateway for its connected VLT peer as shown in the image below. Even though the
gateway address of the packet is dierent, Peer-1 routes the packet to its destination on behalf of Peer-2 to avoid sub-optimal routing.
Figure 134. Packets with peer routing enabled
Benets of Peer Routing
•
• Avoids sub-optimal routing
• Reduces latency by avoiding another hop in the trac path.
1004
Virtual Link Trunking (VLT)