Service Manual
Port-based ACLs These ACLs are applied on all three port modes: on ports directly connected to an FCF, server-facing
ENode ports, and bridge-to-bridge links. Port-based ACLs take precedence over global ACLs.
FCoE-generated
ACLs
These take precedence over user-configured ACLs. A user-configured ACL entry cannot deny FCoE and
FIP snooping frames.
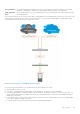
The following illustration shows a switch used as a FIP snooping bridge in a converged Ethernet network. The top-of-rack (ToR)
switch operates as an FCF for FCoE traffic. The switch operates as a lossless FIP snooping bridge to transparently forward
FCoE frames between the ENode servers and the FCF switch.
Figure 42. FIP Snooping on a Dell EMC Networking Switch
The following sections describe how to configure the FIP snooping feature on a switch:
● Allocate CAM resources for FCoE.
● Perform FIP snooping (allowing and parsing FIP frames) globally on all VLANs or on a per-VLAN basis.
● To assign a MAC address to an FCoE end-device (server ENode or storage device) after a server successfully logs in, set
the FCoE MAC address prefix (FC-MAP) value an FCF uses. The FC-MAP value is used in the ACLs installed in bridge-to-
bridge links on the switch.
● To provide more port security on ports that are directly connected to an FCF and have links to other FIP snooping bridges,
set the FCF or Bridge-to-Bridge Port modes.
● To ensure that they are operationally active, check FIP snooping-enabled VLANs.
FIP Snooping
323