White Papers
6 Using MLAG in Dell Networking N-Series Switches | version 1.5
1 Introduction
Dell Networking provides customers with the most efficient modern networking equipment at the
lowest cost for data center, campus, and remote networks. Dell servers, storage, and networking
products with Dell Solutions and Services enable organizations to achieve unique business goals,
improve competitiveness and better serve their customers.
Remote
Data Centers
Dell
Servers
Dell
Storage
Data Center
Dell Network
Controllers
and Security
Campus
Remote/Branch
Office
VRTX
Dell Campus
Networking
Internet
Dell Data Center
Networking
Public Cloud
Storage
Network
WAN
Comprehensive Modern Network
To achieve this, one needs a fault-tolerant and high-bandwidth network. To this end, Dell Networking N-
Series switches support a networking feature called multi-switch link aggregation (MLAG).
MLAG provides an active-active split aggregation deployment across two switches acting as one, creating a
more resilient network with higher bandwidth capabilities. This guide discusses MLAGs, how and when to use
them, caveats to their use, and instructions for their implementation.
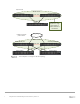
Figure 2 shows two very basic examples of MLAG domains. Both examples show MLAG peer switches linked
with a special LAG (one or more cables as denoted by red lines in many figures in this document), called a
peer link. The peer link can use any non-management port on the switch. With the peer link configured, the
two switches appear as a single switch to partner switches upstream and downstream. Each partner switch
contains MLAGs that are simply Link Aggregation Groups (LAGs) whose cables split between the two peers.
With MLAG enabled, switch firmware automatically assigns primary and secondary peer roles.