Reference Guide
576 | Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Last clearing of "show interface" counters 00:01:28
Queueing strategy: fifo
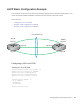
Important Points about Shared LAG State Tracking
• This feature is available for static and dynamic LAGs.
• Only a LAG can be a member of a failover group.
• Shared LAG State Tracking can be configured on one side of a link or on both sides.
• If a LAG that is part of a failover group is deleted, the failover group is deleted.
• If a LAG moves to the down state due to this feature, its members may still be in the up state.
Configure LACP as Hitless
Configure LACP as Hitless is supported only on platforms: c e
LACP on Dell Force10 systems can be configured to be hitless. When configured as hitless, there is no
noticeable impact on dynamic LAG state upon an RPM failover. Critical LACP state information is
synchronized between the two RPMs. Dynamic LAG interfaces in a redundant pair can be in a hitless
LACP configuration.
Configure LACP to be hitless using the command
redundancy protocol lacp from CONFIGURATION
mode, as shown in the following example.
FTOS(conf)#redundancy protocol lacp
FTOS#show running-config redundancy
!
redundancy protocol lacp
FTOS#
FTOS#show running-config interface gigabitethernet 0/12
!
interface GigabitEthernet 0/12
no ip address
!
port-channel-protocol LACP
port-channel 200 mode active
no shutdown
Note: The set of console messages shown in Message 1 appear only if Shared LAG State Tracking is
configured on that router (the feature can be configured on one or both sides of a link). For example, in
previous illustration, if Shared LAG State Tracking is configured on R2 only, then no messages appear on
R4 regarding the state of LAGs in a failover group.