User manual
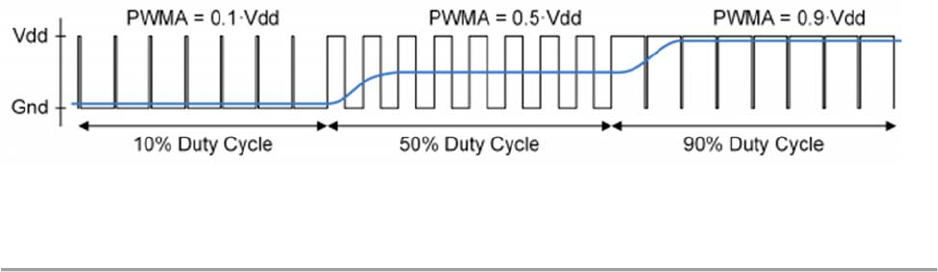
The PWM signal must be integrated to define an analog voltage. The low-pass filter 3dB
frequency should be an order of magnitude lower than the PWM frequency, so that signal energy
at the PWM frequency is filtered from the signal. For example, if an audio signal must contain
up to 5 KHz of frequency information, then the PWM frequency should be at least 50 KHz (and
preferably even higher). In general, in terms of analog signal fidelity, the higher the PWM
frequency, the better. Figure 13.1.2 shows a representation of a PWM integrator producing an
output voltage by integrating the pulse train. Note the steady-state filter output signal amplitude
ratio to Vdd is the same as the pulse-width duty cycle (duty cycle is defined as pulse-high time
divided by pulse-window time).
Figure 13.1.2. PWM Output Voltage.
14 Reset Sources
14.1 Power-on Reset
The Zynq PS supports external power-on reset signals. The power-on reset is the master reset of
the entire chip. This signal resets every register in the device capable of being reset. The Arty Z7
drives this signal from the PGOOD signal of the TPS65400 power regulator in order to hold the
system in reset until all power supplies are valid.
14.2 Program Push Button Switch
A PROG push switch, labeled PROG, toggles Zynq PROG_B. This resets the PL and causes
DONE to be de-asserted. The PL will remain unconfigured until it is reprogrammed by the
processor or via JTAG.
14.3 Processor Subsystem Reset
The external system reset, labeled SRST, resets the Zynq device without disturbing the debug
environment. For example, the previous break points set by the user remain valid after system
reset. Due to security concerns, system reset erases all memory content within the PS, including
the OCM. The PL is also cleared during a system reset. System reset does not cause the boot
mode strapping pins to be re-sampled.










