User manual
The pins connected directly to the Zynq PL can be used as general purpose inputs or outputs.
These pins include the I2C, SPI, and general purpose I/O pins. There are 200 Ohm series
resistors between the FPGA and the digital I/O pins to help provide protection against accidental
short circuits (with the exception of the AN5-AN0 signals, which have no series resistors, and
the AN6-AN12 signals, which have 100 Ohm series resistors). The absolute maximum and
recommended operating voltages for these pins are outlined in the table below.
IO26-IO41 and A (IO42) are not accessible on the Arty Z7-7010. Also, AN0-AN5 cannot be
used as Digital I/O on the Arty Z7-7010. This is due to fewer number of I/O pins being available
on the Zynq 7010 than on the Zynq 7020.
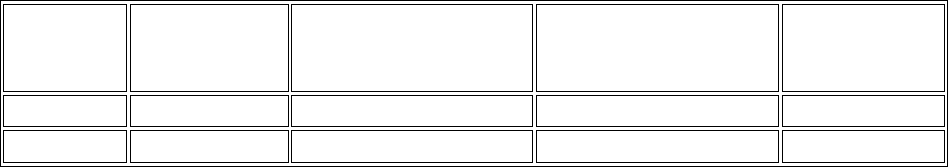
Absolute
Minimum
Voltage
Recommended
Minimum Operating
Voltage
Recommended
Maximum Operating
Voltage
Absolute
Maximum
Voltage
Powered
-0.4 V -0.2 V 3.4 V 3.75 V
Unpowered
-0.4 V N/A N/A 0.55 V
Table 16.1.1. Shield Digital Voltages.
For more information on the electrical characteristics of the pins connected to the Zynq PL,
please see the Zynq-7000 datasheet from Xilinx.
16.2 Shield Analog I/O
The pins labeled A0-A11 and V_P/V_N are used as analog inputs to the XADC module of the
Zynq. The Zynq expects that the inputs range from 0-1 V. On the pins labeled A0-A5 we use an
external circuit to scale down the input voltage from 3.3V. This circuit is shown in Figure 16.2.1.
This circuit allows the XADC module to accurately measure any voltage between 0V and 3.3V
(relative to the Arty Z7's GND) that is applied to any of these pins. If you wish to use the pins
labeled A0-A5 as Digital inputs or outputs, they are also connected directly to the Zynq PL
before the resistor divider circuit (also shown in Figure 16.2.1) on the Arty Z7-7020. This
additional connection is not made on the Arty Z7-7010, which is why these signals can only be
used as analog inputs on that variant.










