User manual
Table Of Contents
- Zynq-7000 All Programmable SoC
- Table of Contents
- Ch. 1: Introduction
- Ch. 2: Signals, Interfaces, and Pins
- Ch. 3: Application Processing Unit
- Ch. 4: System Addresses
- Ch. 5: Interconnect
- Ch. 6: Boot and Configuration
- Ch. 7: Interrupts
- Ch. 8: Timers
- Ch. 9: DMA Controller
- Introduction
- Functional Description
- DMA Transfers on the AXI Interconnect
- AXI Transaction Considerations
- DMA Manager
- Multi-channel Data FIFO (MFIFO)
- Memory-to-Memory Transfers
- PL Peripheral AXI Transactions
- PL Peripheral Request Interface
- PL Peripheral - Length Managed by PL Peripheral
- PL Peripheral - Length Managed by DMAC
- Events and Interrupts
- Aborts
- Security
- IP Configuration Options
- Programming Guide for DMA Controller
- Programming Guide for DMA Engine
- Programming Restrictions
- System Functions
- I/O Interface
- Ch. 10: DDR Memory Controller
- Introduction
- AXI Memory Port Interface (DDRI)
- DDR Core and Transaction Scheduler (DDRC)
- DDRC Arbitration
- Controller PHY (DDRP)
- Initialization and Calibration
- DDR Clock Initialization
- DDR IOB Impedance Calibration
- DDR IOB Configuration
- DDR Controller Register Programming
- DRAM Reset and Initialization
- DRAM Input Impedance (ODT) Calibration
- DRAM Output Impedance (RON) Calibration
- DRAM Training
- Write Data Eye Adjustment
- Alternatives to Automatic DRAM Training
- DRAM Write Latency Restriction
- Register Overview
- Error Correction Code (ECC)
- Programming Model
- Ch. 11: Static Memory Controller
- Ch. 12: Quad-SPI Flash Controller
- Ch. 13: SD/SDIO Controller
- Ch. 14: General Purpose I/O (GPIO)
- Ch. 15: USB Host, Device, and OTG Controller
- Introduction
- Functional Description
- Programming Overview and Reference
- Device Mode Control
- Device Endpoint Data Structures
- Device Endpoint Packet Operational Model
- Device Endpoint Descriptor Reference
- Programming Guide for Device Controller
- Programming Guide for Device Endpoint Data Structures
- Host Mode Data Structures
- EHCI Implementation
- Host Data Structures Reference
- Programming Guide for Host Controller
- OTG Description and Reference
- System Functions
- I/O Interfaces
- Ch. 16: Gigabit Ethernet Controller
- Ch. 17: SPI Controller
- Ch. 18: CAN Controller
- Ch. 19: UART Controller
- Ch. 20: I2C Controller
- Ch. 21: Programmable Logic Description
- Ch. 22: Programmable Logic Design Guide
- Ch. 23: Programmable Logic Test and Debug
- Ch. 24: Power Management
- Ch. 25: Clocks
- Ch. 26: Reset System
- Ch. 27: JTAG and DAP Subsystem
- Ch. 28: System Test and Debug
- Ch. 29: On-Chip Memory (OCM)
- Ch. 30: XADC Interface
- Ch. 31: PCI Express
- Ch. 32: Device Secure Boot
- Appx. A: Additional Resources
- Appx. B: Register Details
- Overview
- Acronyms
- Module Summary
- AXI_HP Interface (AFI) (axi_hp)
- CAN Controller (can)
- DDR Memory Controller (ddrc)
- CoreSight Cross Trigger Interface (cti)
- Performance Monitor Unit (cortexa9_pmu)
- CoreSight Program Trace Macrocell (ptm)
- Debug Access Port (dap)
- CoreSight Embedded Trace Buffer (etb)
- PL Fabric Trace Monitor (ftm)
- CoreSight Trace Funnel (funnel)
- CoreSight Intstrumentation Trace Macrocell (itm)
- CoreSight Trace Packet Output (tpiu)
- Device Configuration Interface (devcfg)
- DMA Controller (dmac)
- Gigabit Ethernet Controller (GEM)
- General Purpose I/O (gpio)
- Interconnect QoS (qos301)
- NIC301 Address Region Control (nic301_addr_region_ctrl_registers)
- I2C Controller (IIC)
- L2 Cache (L2Cpl310)
- Application Processing Unit (mpcore)
- On-Chip Memory (ocm)
- Quad-SPI Flash Controller (qspi)
- SD Controller (sdio)
- System Level Control Registers (slcr)
- Static Memory Controller (pl353)
- SPI Controller (SPI)
- System Watchdog Timer (swdt)
- Triple Timer Counter (ttc)
- UART Controller (UART)
- USB Controller (usb)
Zynq-7000 AP SoC Technical Reference Manual www.xilinx.com 673
UG585 (v1.11) September 27, 2016
Chapter 24: Power Management
24.3 Programming Guides
24.3.1 System Modules
The power management features of the Zynq-7000 AP SoC's system modules are described in detail
in their respective chapter. Please refer to Table 24-4 for an overview and further references.
24.3.2 Peripherals
The primary peripheral power management mechanisms are clock scaling and gating. Chapter 25,
Clocks describes the system clocks and how they can be controlled through dividers, gates, and
multiplexers. Table 24-2 gives a brief overview of the power management capabilities for the device
subsystems. Every peripheral includes clock gating and, in some cases, low-power states.
With all these pieces working together, the system-level sleep mode is defined. (Refer to section
24.4 Sleep Mode.) In sleep mode the whole chip enters a low-power state, waiting for a wake-up
event to continue operation.
Peripheral Clock Gating
For peripherals with an independent clock domain for the interconnect, disable the device's
interconnect clock last and enable it first to avoid accesses to inaccessible register areas. See
Chapter 25, Clocks and the respective chapter for a peripheral for additional details.
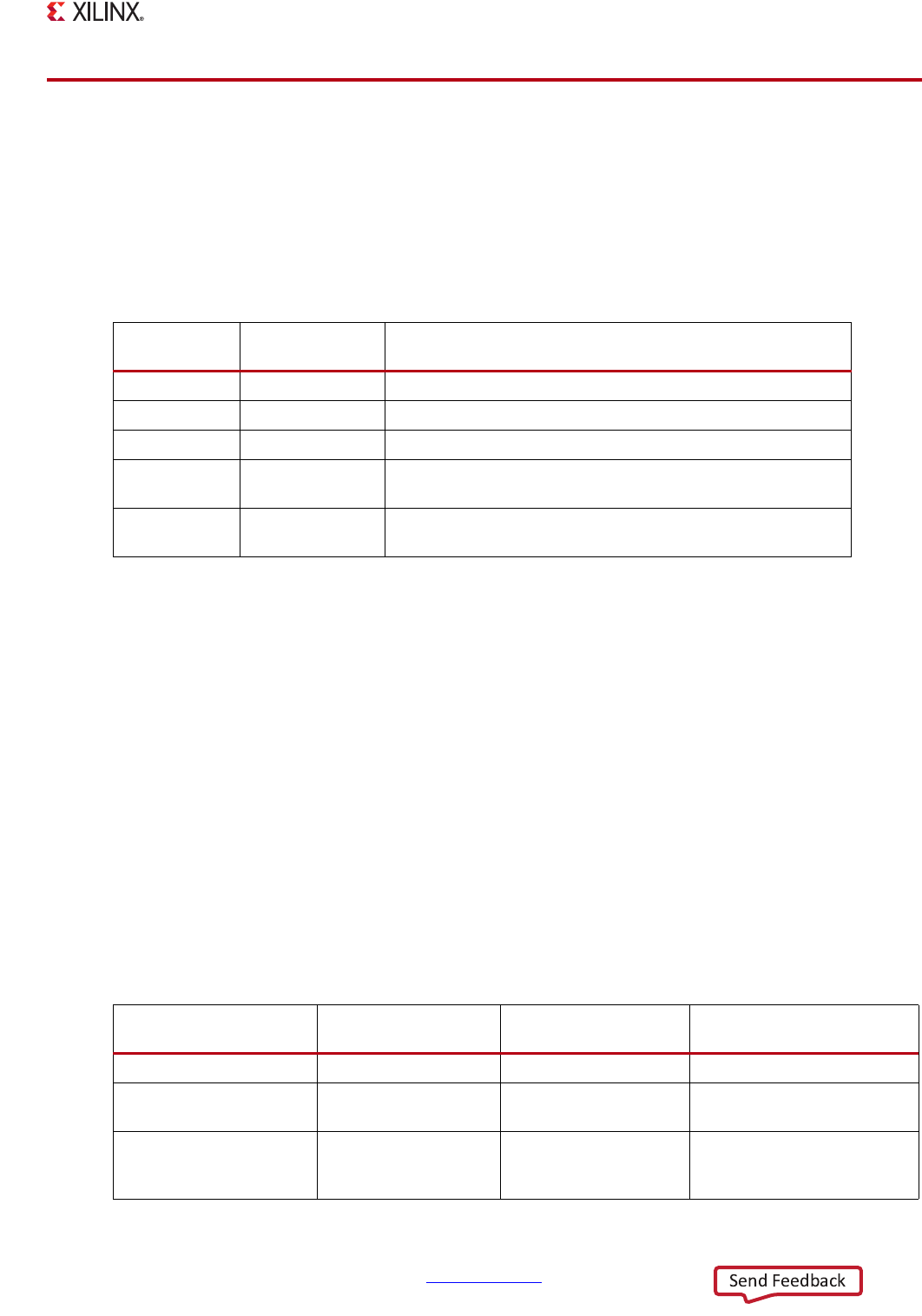
Table 24-1: Power Management for System Modules
System Module
Clocked in
Standby Mode
Description
APU Yes See Chapter 3, Application Processing Unit.
SCU (with GIC) Yes See Chapter 3, Application Processing Unit.
L2-Cache Yes See Chapter 3, Application Processing Unit.
Interconnect Yes Clocks are stopped automatically if enabled, refer to
Chapter 25, Clocks.
Peripherals Depends Peripheral used as a wake-up source must be clocked, refer to
Table 24-2.
Table 24-2: Power Management for Peripheral Controls
Peripheral Wake-up Source
Clock Gating Low-Power
Mode
Other Low-Power Modes
PCAP No No None
Timers
Yes
Chapter 8, Timers
Yes
Chapter 25, Clocks
None
DMA Controller No
Yes
Section 9.6 System
Functions
None










