Wireless Modem Router User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Version 2.4
- Before You Use
- Unpacking
- Features
- ADSL Compliance
- ADSL2 Compliance
- ADSL2+ Compliance
- Wireless LAN Compliance
- ATM Features
- Bridging Features
- Routing Features
- Security Features
- Configuration and Management
- Subscription for ADSL Service
- Notes and Cautions
- Chapter 1: Overview
- Physical Outlook
- Front Panel
- LED Indicators
- Rear Panel
- Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
- System Requirement
- Choosing a place for the ADSL Router
- Connecting the ADSL Router
- USB Driver Installation
- For Windows ME
- For Windows 2000
- For Windows XP
- For Windows Vista
- Uninstalling the USB Driver
- For Windows ME
- For Windows 2000
- For Windows XP
- For Windows Vista
- Setting up TCP/IP
- For Windows 98
- For Windows ME
- For Windows NT
- For Windows 2000
- For Windows XP
- For Windows Vista
- Renewing IP Address on Client PC
- For Windows 98/ME
- For Windows NT/2000/XP
- For Windows Vista
- Chapter 3: Accessing the Internet
- PPP over ATM (PPPoA) Mode
- Description:
- Configuration:
- PPP over ATM (PPPoA) IP Extension Mode
- Description:
- Configuration:
- PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) Mode
- Description:
- Configuration:
- PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) IP Extension Mode
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Numbered IP over ATM (IPoA)
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Numbered IP over ATM (IPoA)+NAT
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Unnumbered IP over ATM (IPoA)
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Unnumbered IP over ATM (IPoA)+NAT
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Bridge Mode
- Description:
- Configuration:
- MER
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Chapter 4: Web Configuration
- Using Web-Based Manager
- Outline of Web Manager
- To Have the New Settings Take Effect
- Language
- Quick Start
- Connect to Internet
- Quick Setup
- Connection Type
- PPP over ATM/ PPP over Ethernet
- IP over ATM
- Bridging
- Status
- Overview
- ADSL Line
- ADSL BER Test
- Internet Connection
- Traffic Statistics
- DHCP Table
- Wireless Clients
- Routing Table
- ARP Table
- Advanced Setup
- Local Network – IP Address
- Local Network – DHCP Server
- Local Network – UPnP
- Local Network – IGMP Snooping
- Internet – Connections
- Adding a New One
- Internet – DNS Server
- Internet – IGMP Proxy
- Internet – ADSL
- IP Routing – Static Route
- Adding a New One
- Remove Static Route
- Example – Static Route
- IP Routing – Dynamic Routing
- Operation: There are two modes for you to choose, Active and Passive. Select Active for transmitting and receiving data, or select Passive for receiving data only.
- Virtual Server – Port Forwarding
- IP Address seen by Internet Users
- Add New Port Forwarding
- Virtual Server – Port Triggering
- Virtual Server – DMZ Host
- Virtual Server – Dynamic DNS
- Virtual Server – Static DNS
- NAT ALG Configuration
- Firewall
- Firewall – Bridge Filtering
- Firewall – IP Filtering
- Quality of Service
- Quality of Service – Bridge QoS
- Quality of Service – IP QoS
- Port Mapping
- Wireless
- Basic Settings
- Security
- For 64-bit WEP/128-bit WEP
- For 802.1X Wireless Network
- 802.1x environment Configuration
- For WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
- For WPA-PSK; WPA2-PSK; Mixed WPA2/WPA-PSK
- For WPA-2; Mixed WPA2/WPA
- Access Control
- Repeater
- Management
- Diagnostics
- Management Accounts
- Management Control – From Remote
- Management Control – From Local
- TR-069 Client Configuration
- Identify the Validation of Certificate from ACS
- Internet Time
- System Log
- Configuring System Log
- Example
- System Log Configuration
- Viewing System Log – Remote Side (Server)
- Viewing System Log – Local Side (ADSL Router)
- Backup Config
- Update Firmware
- Reset Router
- UPnP for XP
- Chapter 5: Troubleshooting
- Problems with LAN
- Problems with WAN
- Problems with Upgrading
- Chapter 6: Glossary
- ARP (Address Resolution Protocol )
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- LAN (Local Area Network) & WAN (Wide Area Network)
- NAT (Network Address Translation) IP Address
- Private IP Address
- Public IP Address
- PVC (Permanent Virtual Circuit)
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
- Virtual Server
- VPI (Virtual Path Identifier) & VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier)
- Appendix A: Specifications
- Appendix B: Client Setup for 802.1x, WPA, and WPA-PSK
- Retreiving Client Certificate
- Enabling 802.1x Authentication and Security
- Enabling WPA Authentication and Security
- Enabling WPA-PSK Authentication and Security
ADSL Router User Manual
98
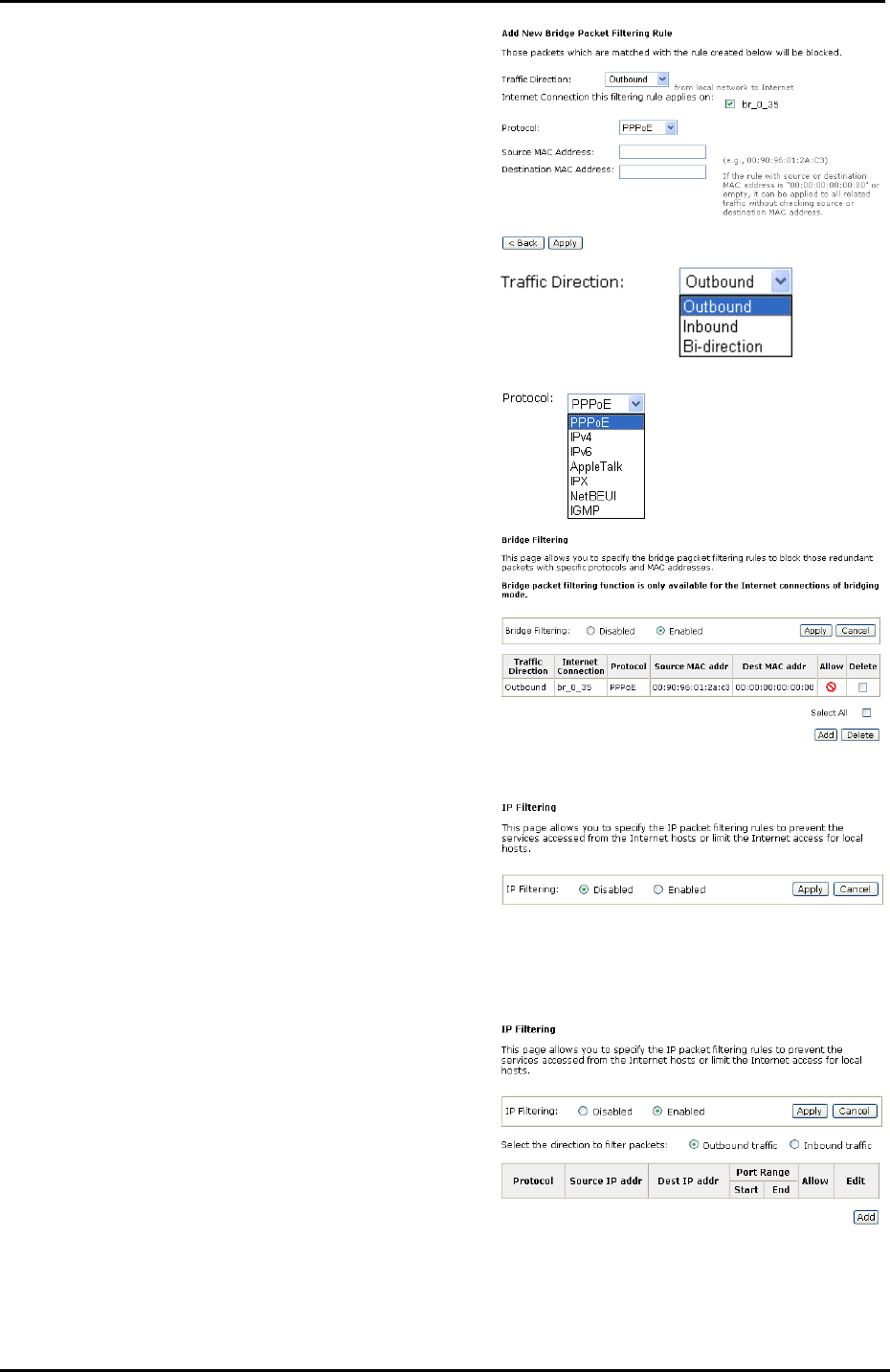
Select traffic direction from the drop
down menu, and check the network
interface which you want this rule to
apply on. Then, choose a protocol and
define the source or destination MAC
address which you want to control.
There are three options for traffic
direction: Outbound means from local
network to Internet; Inbound means
from Internet to local network;
Bi-direction includes both directions.
The protocols that you can choose is
listed as the right figure shows. Select
one proper protocol for this bridge
filtering rule.
For example, if we choose Outbound,
check br_0_35, select PPPoE as
protocol, and enter 00:90:96:01:2A:C3
into the Source MAC Address field,
then after clicking Apply, we will see
the result as shown in the right.
You can use Add or Delete button to
maintain the bridge filtering rules.
Firewall – IP Filtering
This page allows you to specify the IP
packet filtering rules to prevent the
services accessed from the Internet
hosts or limit the Internet access for
local hosts.
Choose Disabled to disable the
firewall function. Click Enabled to
invoke the settings that you set in this
web page.
To initiate the IP Filtering, please
select the Enabled radio button and
click Apply.
Select the direction to filter
packets:
Inbound means the data is transferred
from outside onto your computer.
Outbound means the data is
transferred from your computer onto
outside through Internet. Please
choose Outbound traffic or Inbound
traffic as the direction for filtering
packets.
To add a new Filtering rule, click Add.










