Wireless Modem Router User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Version 2.4
- Before You Use
- Unpacking
- Features
- ADSL Compliance
- ADSL2 Compliance
- ADSL2+ Compliance
- Wireless LAN Compliance
- ATM Features
- Bridging Features
- Routing Features
- Security Features
- Configuration and Management
- Subscription for ADSL Service
- Notes and Cautions
- Chapter 1: Overview
- Physical Outlook
- Front Panel
- LED Indicators
- Rear Panel
- Chapter 2: System Requirement and Installation
- System Requirement
- Choosing a place for the ADSL Router
- Connecting the ADSL Router
- USB Driver Installation
- For Windows ME
- For Windows 2000
- For Windows XP
- For Windows Vista
- Uninstalling the USB Driver
- For Windows ME
- For Windows 2000
- For Windows XP
- For Windows Vista
- Setting up TCP/IP
- For Windows 98
- For Windows ME
- For Windows NT
- For Windows 2000
- For Windows XP
- For Windows Vista
- Renewing IP Address on Client PC
- For Windows 98/ME
- For Windows NT/2000/XP
- For Windows Vista
- Chapter 3: Accessing the Internet
- PPP over ATM (PPPoA) Mode
- Description:
- Configuration:
- PPP over ATM (PPPoA) IP Extension Mode
- Description:
- Configuration:
- PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) Mode
- Description:
- Configuration:
- PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) IP Extension Mode
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Numbered IP over ATM (IPoA)
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Numbered IP over ATM (IPoA)+NAT
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Unnumbered IP over ATM (IPoA)
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Unnumbered IP over ATM (IPoA)+NAT
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Bridge Mode
- Description:
- Configuration:
- MER
- Description:
- Configuration:
- Chapter 4: Web Configuration
- Using Web-Based Manager
- Outline of Web Manager
- To Have the New Settings Take Effect
- Language
- Quick Start
- Connect to Internet
- Quick Setup
- Connection Type
- PPP over ATM/ PPP over Ethernet
- IP over ATM
- Bridging
- Status
- Overview
- ADSL Line
- ADSL BER Test
- Internet Connection
- Traffic Statistics
- DHCP Table
- Wireless Clients
- Routing Table
- ARP Table
- Advanced Setup
- Local Network – IP Address
- Local Network – DHCP Server
- Local Network – UPnP
- Local Network – IGMP Snooping
- Internet – Connections
- Adding a New One
- Internet – DNS Server
- Internet – IGMP Proxy
- Internet – ADSL
- IP Routing – Static Route
- Adding a New One
- Remove Static Route
- Example – Static Route
- IP Routing – Dynamic Routing
- Operation: There are two modes for you to choose, Active and Passive. Select Active for transmitting and receiving data, or select Passive for receiving data only.
- Virtual Server – Port Forwarding
- IP Address seen by Internet Users
- Add New Port Forwarding
- Virtual Server – Port Triggering
- Virtual Server – DMZ Host
- Virtual Server – Dynamic DNS
- Virtual Server – Static DNS
- NAT ALG Configuration
- Firewall
- Firewall – Bridge Filtering
- Firewall – IP Filtering
- Quality of Service
- Quality of Service – Bridge QoS
- Quality of Service – IP QoS
- Port Mapping
- Wireless
- Basic Settings
- Security
- For 64-bit WEP/128-bit WEP
- For 802.1X Wireless Network
- 802.1x environment Configuration
- For WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
- For WPA-PSK; WPA2-PSK; Mixed WPA2/WPA-PSK
- For WPA-2; Mixed WPA2/WPA
- Access Control
- Repeater
- Management
- Diagnostics
- Management Accounts
- Management Control – From Remote
- Management Control – From Local
- TR-069 Client Configuration
- Identify the Validation of Certificate from ACS
- Internet Time
- System Log
- Configuring System Log
- Example
- System Log Configuration
- Viewing System Log – Remote Side (Server)
- Viewing System Log – Local Side (ADSL Router)
- Backup Config
- Update Firmware
- Reset Router
- UPnP for XP
- Chapter 5: Troubleshooting
- Problems with LAN
- Problems with WAN
- Problems with Upgrading
- Chapter 6: Glossary
- ARP (Address Resolution Protocol )
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- LAN (Local Area Network) & WAN (Wide Area Network)
- NAT (Network Address Translation) IP Address
- Private IP Address
- Public IP Address
- PVC (Permanent Virtual Circuit)
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
- Virtual Server
- VPI (Virtual Path Identifier) & VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier)
- Appendix A: Specifications
- Appendix B: Client Setup for 802.1x, WPA, and WPA-PSK
- Retreiving Client Certificate
- Enabling 802.1x Authentication and Security
- Enabling WPA Authentication and Security
- Enabling WPA-PSK Authentication and Security
ADSL Router User Manual
84
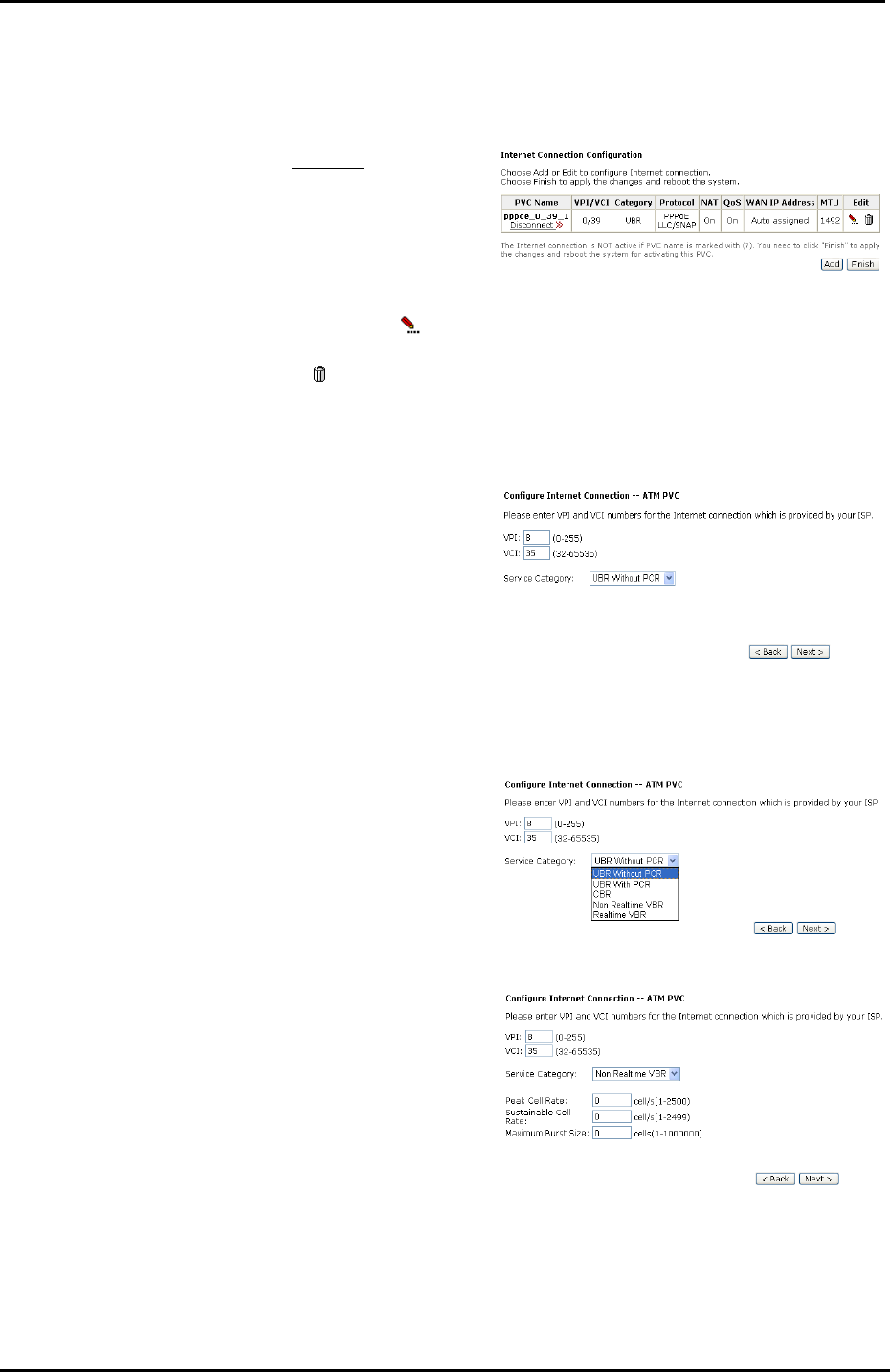
Internet – Connections
To set WAN settings for each service, please open Advanced– Internet. This page
allows you to edit, to remove, or to add WAN settings.
If you click the Connect
hyperlink
under the PVC Name item, the system
will connect to WAN automatically. If
the WAN connection is OK, you can
check the detailed information directly.
You can add new PVC(s) by clicking
the Add button, edit the settings for
the present PVC by clicking
in the
Edit column, or delete the existing
PVC by pressing
icon.
Adding a New One
To add a new WAN connection, please click the Add button. The following screen
appears.
VPI (Virtual Path Identifier):
Identifies the virtual path between
endpoints in an ATM network. The
valid range is from 0 to 255. Please
refer to the value that your ISP
provides.
VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier):
Identifies the virtual channel endpoints
in an ATM network. The valid range is
from 32 to 65535 (1 to 31 is reserved
for well-known protocols). Please refer
to the value that your ISP provides.
Service Category:
It decides the size and rate for the
packets of the data in different service
type. There are five categories
provided here for your selection,
shown as the drop-down menu in the
right column.
If you select UBR with PCR or CBR,
you have to offer the value for the
peak cell rate.
If you choose Non Realtime VBR, or
Realtime VBR, you have to key in the
value for the peak cell rate,
sustainable cell rate, and maximum
burst size.
As you can see in the right figure, the
range for Peak Cell Rate is from 1 to
2500; the value for Sustainable Cell
Rate ranges from 1 to 2499 and must
be smaller than Peak Cell Rate, and
the range for Maximum Burst Size is
from 1 to 1000000.










