Instruction Manual
Instruction Hexadecimal
Opcode
Instruction
Size (Bytes)
CPU Cycles
Required
Affect on
Carry Flag
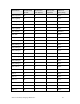
POP !15 CF 1 4 None
POP !16 D0 1 4 None
POP !17 D1 1 4 None
POP !18 D2 1 4 None
POP !19 D3 1 4 None
POP !20 D4 1 4 None
POP !21 D5 1 4 None
POP !22 D6 1 4 None
POP !23 D7 1 4 None
POP !TOS E6 1 4 None
Examples:
The following example moves the value 23 from TOS into the element following
NEXT. The instruction overwrites the destination element and consumes TOS;
the remainder of the stack remains unchanged.
Example APEXP ; ( -- )
pushs #1 ; ( 1 )
pushs #2 ; ( 2, 1 )
pushs #3 ; ( 3, 2, 1 )
push #d’23 ; ( d’23, 3, 2, 1 )
pop [dsp][-1] ; ( 3, d’23, 1 )
dealloc #3 ; ( )
The following example clears the general-purpose register R0.
R0 EQU 8
Example APEXP ; ( -- )
pushs #0 ; ( 0 )
pop !R0 ; ( )
ret ; return to caller
The following example function clears the N-th byte of the base page. N is in the
range 0 to 255. This example assumes that N is in TOS when calling this
function.
Example APEXP ; ( n -- )
pushs #0 ; ( 0, n )
98 Neuron Assembly Language Instruction Statements