Manual
English
9
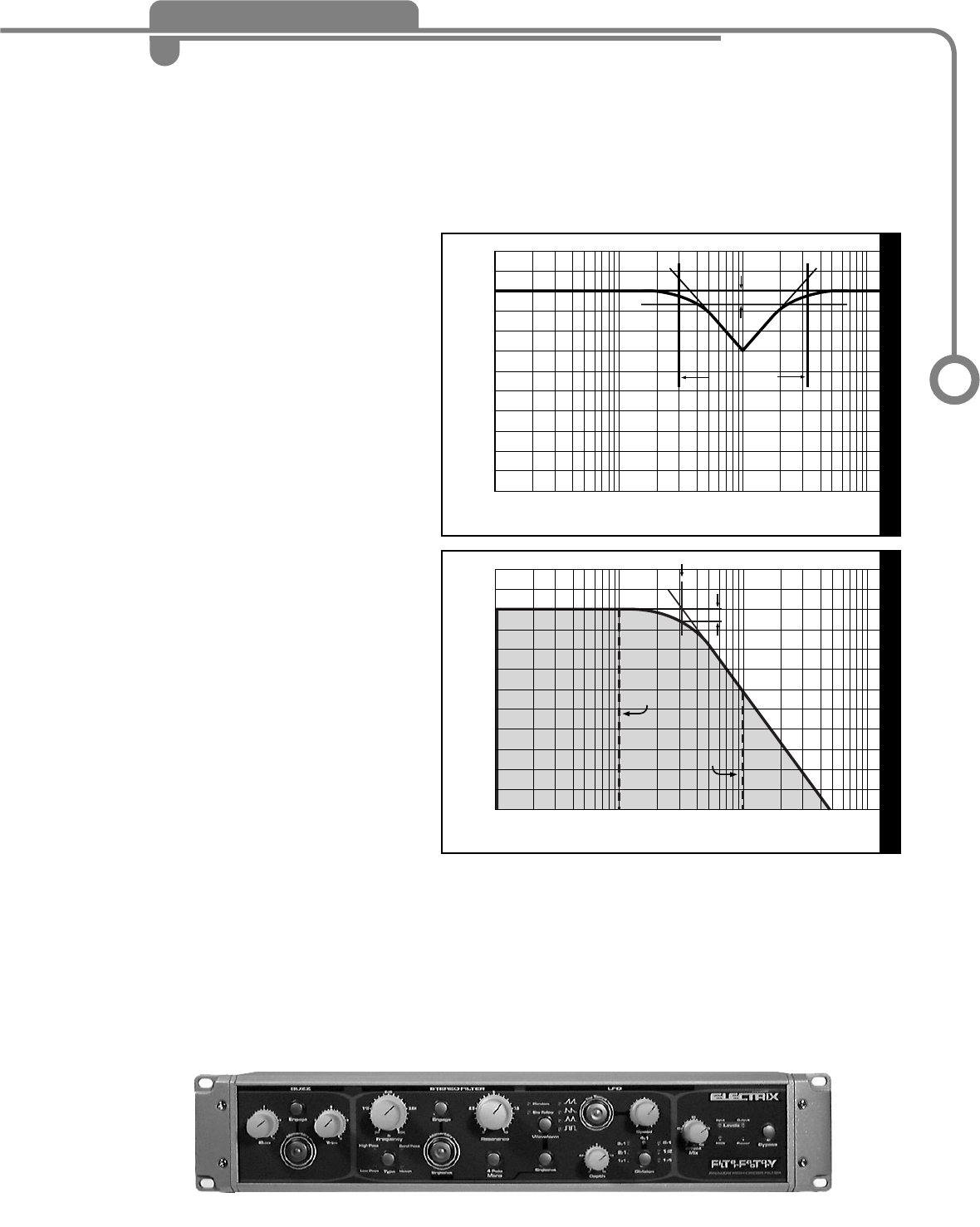
The Low Pass Filter is the most commonly used filter type. This is the kind of filter
you will find on vintage synths and envelope followers. It is useful for controlling the
amount of harmonics or the brightness of a signal. As you sweep the frequency
control, try adding some resonance to make the cutoff frequency more audible.
" Filter Engage: This control toggles the filter on and off. Turning this on restarts
the LFO or triggers it if it is in single shot mode.
" Filter Momentary: This
switch temporarily engages the
stereo filter. Try using it to tap
rhythmic patterns while
adjusting the frequency knob.
Pressing this button also
restarts the LFO.
" Resonance:
This controls the level of the
peak at the resonant frequency
of the filter, i.e. the frequency
you dialed in with the
frequency knob. FilterFactory
was designed to create
extreme effects, so be careful
because the resonance control
is able to cause the filters to
self-oscillate at higher settings.
Self oscillation produces a loud
tone at the resonant frequency.
It sounds a lot like sustained
feedback.
" 4 Pole Mono: The
FilterFactory operates in
a Stereo 2 Pole filter per
channel mode, ( unless you
switch to 4 Pole mode). When
in Four Pole mode, the
FilterFactory switches into
Mono operation by summing the left and right channels before the
4 pole filter. A two pole filter will give you a gentler response, in technical terms it is
defined as a 12dB/octave filter. A 4 pole or 24dB/octave filter will give you a much
steeper filter response that will sound more pronounced.
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
10 20 30 50 70 100 200 300 500 700 1000 2,000 3,000 5,000 7,000 10,000
dB
FREQUENCY
Bandwidth
-3 dB
Fig. 3: Notch Filter
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
10 20 30 50 70 100 200 300 500 700 1000 2,000 3,000 5,000 7,000 10,000
dB
FREQUENCY
-3 dB
Cutoff point
100 Hz
Sine wave
1,000 Hz
Sine wave
Fig. 4: Low Pass Filter
FRONT PANEL2.1










