Network Hardware User Manual
HARSFEN0602
MO
Brake
1
Released
BP[2] BP[1]
Time (msec)
Motor
controlled
to stop
Motor
controlled
to stop
Motion
Commands
N.A.
According tomotion
programming
N.A.
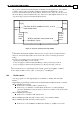
Figure 39: Normal Brake Activation Timing
At the brake activation times (BP[2] msec to disengage, BP[1] msec to engage) the motor is
controlled to complete stop.
If MO=0 is set automatically by an exception, the brake is activated immediately, without
any delay.
14.7 When the motor fails to start
The main reasons for failure to start the motor are:
The physical conditions are not right
The database is not consistent (refer the section "Inconsistent setup data" below)
The following physical conditions are tested before applying voltage to the motor
Power supply under voltage
Power supply over voltage
Amplifier temperature too high
Motor not connected to the servo drive
An active limit switch is programmed to shut the servo drive down.
The motor shall not start if the voltage of the power supply is not within range, or if the servo drive
temperature is too high, or an active switch prevents motor on. The MO command will return the error codes
65 or 66. The failure reason may be read through the status (SR) report.
If the voltage is in range, and the temperature is not excessive, the Amplifier will try to start the motor.
For more details, refer the section "Current amplifier protections".
14.8 Motion faults
Error conditions may cause the Amplifier to shut the motor automatically.
When the motor is shut down automatically,
The MO variable is set to zero
The variable MF is set to reflect the shut down reason.
A flag in the status register (SR) indicates that the motion has been aborted.
The variable MF may reveal why the motor has been shut even if the reason no longer exists. For example, if
the power supply has too large impedance, then in full load its voltage may drop and the servo drive will be
automatically shut down due to under voltage. When the motor is shut, the under voltage disappears.
Another example is that an over voltage is generated due to an insufficient shunt. Again, the over voltage
will disappear when the motor is shut down.
The over or the under voltage conditions that caused the fault are recorded in the MF variable.