Specifications
Computer Architecture and Maintenance (G-Scheme-2014)
not have louse the motherboard’s system bus for data transfer. Whenever data must
be passed through the system bus, the data transfer speed s to the motherboard’s
capability. The CPU can process data much faster by avoiding the bottleneck created by
the system bus.
As it happens, once most programs are open and running, they use very few
resources. When these resources are kept in cache, programs can operate more quickly
and efficiently. All else being equal, cache is so effective in system performance that a
computer running a fast CPU with little cache can have lower benchmarks than a
system running a somewhat slower CPU with more cache.
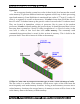
Types of Cache Memory
• Level-1 Cache
• Level-2 Cache
• Level-3 Cache
Level-1
Also called as L1 cache, primary cache, internal cache, or system cache. When
referring to computer processors, L1 cache is cache that is built into the processor and is
the fastest and most expensive cache in the computer. The L1 cache stores the most
critical files that need to be executed and is the first thing the processor looks when
performing an instruction
Ll, or primary cache, is a small, high-speed cache incorporated right onto the
processor’s chip. The Li cache typically ranges in size from 8KB to 64KB and uses the
high-speed SRAM (static RAM) instead of the slower and cheaper DRAM (dynamic
RAM) used for main memory. Using memory cache to hold memory values, or the
most recently used data and instructions means the processor can retrieve the data
from the cache instead of the system’s main memory, which is much slower than the
cache memory.
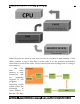
Level 2
L2 is also commonly referred to as secondary cache or external cache. Unlike
Layer 1 cache, L2 cache was located on the motherboard on earlier computers, although
with newer processors it is found on the processor chip. When L2 cache is found on the
processor, if the cache is also on the motherboard, it is more properly known as L3
cache.
Tip: The L2 cache is on the same processor chip and uses the same die as the CPU,
however, it is still not part of the core of the CPU.
Prepared By – Prof. Manoj.kavedia (9860174297 – 9324258878 ) (www.kavediasir.yolasite.com)
65